So I've been tasked by my neural network professor at university to replicate the following research: Intelligent Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Hybrid GA-ANN.
Each chromosome represents a possible net, more specifically, a possible MLP network. They've used a binary convention, and have used $P = 15$ bits for the random initial weight generator, $Q=2$ bits for the number of nodes and $R = 9$ bits for feature selection.
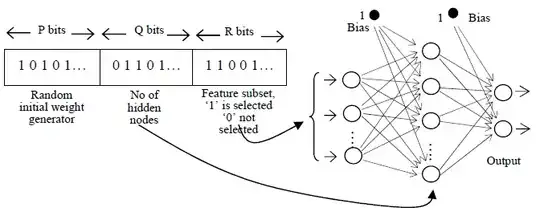
P bits random initial weight generator allows 2P different combinations of the initial weight. The numbers of hidden nodes (i.e. represented by Q bits) permit the GA to explore up to a maximum of 2Q hidden nodes’ size. For the representation of the feature subset, the value of R is set to the number of full feature size. Value ‘1’ or ‘0’ indicates if the feature at that particular location is selected or otherwise.
Decode each chromosome in the population to obtain the selected feature subset, hidden node size and random generator.
I don't understand why they say with $P$ bits, there's $2*P$ combinations, wouldn't it be $2^P$? Also, I can't grasp how they decoded the $15 P$ bits into the net for the weight generation. I've searched everywhere but I can't find anything specific. What I thought to do was to transform the $15$ bits into a decimal number and use it as a specific seed for rand and randn function in Matlab, through which I make random initial weights.