Host: Ubuntu
Choose the folder that is to be shared (the same way as below - open VM settings on Your host and choose). Lets say it is (folder on Your host which You want to see from Win7 guest):
/home/misery
This tutorial covers the answer. After adding Your Ubuntu folder to shared start or reboot Your Win7 VM You should search Your local area network (in Win7 guest; wait until it has searched it - the green progress bar). After that network disk should appear.
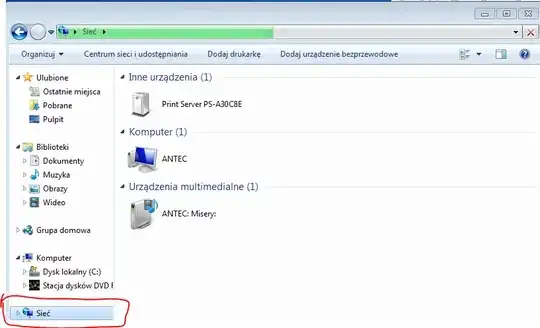
On my PC it was found with no further steps. In case of problems please refer to the tutorial.
Host: Win7, Guest OS: Ubuntu
First go to Your virtual machines settings:

Add the folder You wish to share and name it (it will automatically name it). Here the Win7 path to my folder is C:\Misery and the name is Misery
Then mark Auto mount option to mount it always when starting Your VM.
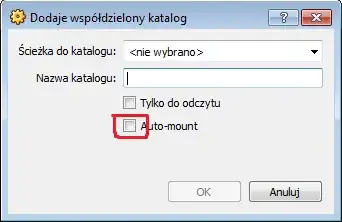
And basically that's it. Now start Your virtual machine. This tutorial explains the rest, in short You need to create the folder that will be Your mounting point (on the guest). Let's say it will be GMisery on Your ubuntu. So Create it in Your user directory. So now we have existing empty folder on guest OS:
/home/misery/GMisery
Next open Your terminal and write:
sudo mount -t vboxsf -o uid=1000,gid=1000 Misery /home/misery/GMisery
Now it should work. At least id does on my PC :] If no error occured, logout and login again and it should be done.
Please read attached tutorial also.
And in general it is a good idea to install on your host VB extension pack. However it has no influence on the topic discussed here.


