There are two reasons that I can think of why you can't use your Windows partition. Windows often has an issue with hanging on to the partition if it is not shut down completely. Holding down the shift key while shutting down Windows should fix this problem. If you don't want to completely turn off your computer to boot into Windows to completely shut it down and reboot again, I'd check out this answer here.
However, since you are able to read it, this sounds more like a problem with permissions.
Go ahead and check out this article to find out how to mount your NTFS Windows partition to enable permissions. I'd also suggest checking out some of the other links that other users have been suggesting under your comments.
Then, open up your terminal and type up sudo nautilus and then left click on your Windows partition once the file manager pops up. Select Properties and then navigate to the Permissions tab. Then change the Owner and/or Group to your username. Then hit the Change Permissions for Enclosed Files... button on the bottom of the properties window. Then change the Files and Folders permissions to Read and Write for the Owner or Group, whatever you changed earlier.
You can also do the same thing all in the terminal with chown and chmod but that's another answer.
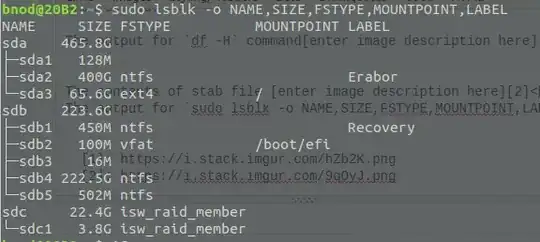
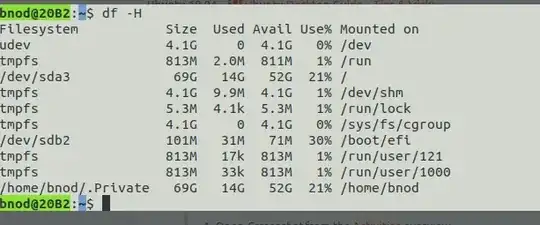
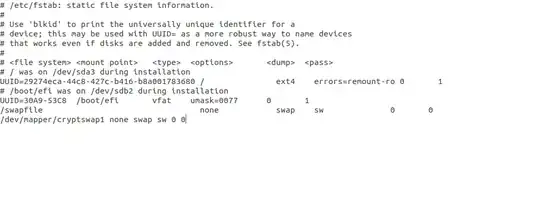
sudo lsblk -o NAME,SIZE,FSTYPE,MOUNTPOINT,LABEL– wjandrea Jul 17 '18 at 17:47