I assume that you want to bind for any bash command.
1.0 First get commands to change workspace from terminal
Go to first workspace. Open terminal and run wmctrl -d | awk '{print $6} for me it yields 0,0 note it as co-ordinates of first workspace.
Move terminal to Next workspace and do above procedure again for all workspaces.
My output after doing above steps
virpara@Ascension:~$ wmctrl -d | awk '{print $6}' #in workspace 1
0,0
virpara@Ascension:~$ wmctrl -d | awk '{print $6}' #in workspace 2
1366,0
virpara@Ascension:~$ wmctrl -d | awk '{print $6}' #in workspace 3
0,768
virpara@Ascension:~$ wmctrl -d | awk '{print $6}' #in workspace 4
1366,768
You may be thinking What we've got after doing this? we have co-ordinates to switch to desired workspace.
We can use wmctrl -o X,Y to switch to respective workspaces. where X,Y are your workspace co-ordinates.
For me, Commands to switch to workspaces are as follows,
For Workspace 1 => wmctrl -o 0,0
For Workspace 2 => wmctrl -o 1366,0
For Workspace 3 => wmctrl -o 0,768
For Workspace 4 => wmctrl -o 1366,768
2.0 Set HotKeys for those commands
How to install AutoKey
Open software center > search for autokey > install AutoKey(GTK)
How to bind any key ?
Step 1 :
Press
Ctrl+
Shift+
N or from
File > Create.. > New Script. Rename with whatever you like.
Step 2 :
Paste below code as shown, I'll bind
Super+
1 to Workspace 1. Replace
wmctrl -o 0,0 with your command.
import os
os.system("wmctrl -o 0,0")

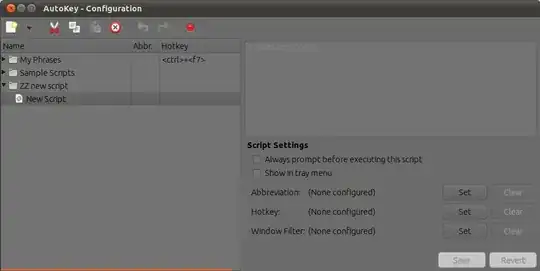
Step 3 :
Then in bottom-right corner there is three
Set buttons to set for
Abbreviation or
Hotkey or
Window Filter. Click second
Set button (because we want to set hotkey).

Step 4 :
Click
Super then Click
Press to Set and hit a key you want to assign(in your case
1. I'm hitting
1).

Step 5 :
Click
OK.
Step 6 :
Click
Save in bottom-right corner.

Try hitting Super+1.
Go to Step 1 : and do this for all commands you got earlier in 1.0 to bind to Super+2, 3, 4 .




