dd is a wonder. It lets you duplicate a hard drive to another, completely zero a hard drive, etc. But once you launch a dd command, there's nothing to tell you of its progress. It just sits there at the cursor until the command finally finishes. So how does one monitor dd's progress?
22 Answers
Update 2016: If you use GNU coreutils >= 8.24 (default in Ubuntu Xenial 16.04 upwards), you can simply add status=progress to your dd command. See method 2 below for details.
Method 1: By using pv
Install pv and put it between input / output only dd commands.
Note: you cannot use it when you already started dd.
From the package description:
pv- Pipe Viewer - is a terminal-based tool for monitoring the progress of data through a pipeline. It can be inserted into any normal pipeline between two processes to give a visual indication of how quickly data is passing through, how long it has taken, how near to completion it is, and an estimate of how long it will be until completion.
Installation
sudo apt-get install pv
Example
dd if=/dev/urandom | pv | dd of=/dev/null
Output
1,74MB 0:00:09 [ 198kB/s] [ <=> ]
You could specify the approximate size with the --size if you want a time estimation.
Example Assuming a 2GB disk being copied from /dev/sdb
Command without pv would be:
sudo dd if=/dev/sdb of=DriveCopy1.dd bs=4096
Command with pv:
sudo dd if=/dev/sdb | pv -s 2G | dd of=DriveCopy1.dd bs=4096
Output:
440MB 0:00:38 [11.6MB/s] [======> ] 21% ETA 0:02:19
Other uses
You can of course use pv directly to pipe the output to stdout:
pv /home/user/bigfile.iso | md5sum
Output
50,2MB 0:00:06 [8,66MB/s] [=======> ] 49% ETA 0:00:06
Note that in this case, pv recognizes the size automatically.
Method 2: New status option added to dd (GNU Coreutils 8.24+)
dd in GNU Coreutils 8.24+ (Ubuntu 16.04 and newer) got a new status option to display the progress:
Example
dd if=/dev/urandom of=/dev/null status=progress
Output
462858752 bytes (463 MB, 441 MiB) copied, 38 s, 12,2 MB/s
From HowTo: Monitor the progress of dd
You can monitor the progress of dd once it's running without halting it by using the kill command to send a signal to the process.
After you start dd, open another terminal and enter either:
sudo kill -USR1 $(pgrep ^dd$)
Or, if you're on BSD or OS X:
sudo kill -INFO $(pgrep ^dd$)
This will display the progress in the dd terminal window without halting the process (by printing to its stderr stream). For example:
# dd if=/dev/urandom of=rando bs=1024 count=1048576
335822+0 records in
335821+0 records out
343880704 bytes (344 MB, 328 MiB) copied, 6.85661 s, 50.2 MB/s
If you would like to get regular updates of the dd progress, then enter:
watch -n5 'sudo kill -USR1 $(pgrep ^dd$)'
watch will probe the dd process every -n seconds (-n5 = 5 seconds) and report without halting it.
Note the proper single quotes in the commands above.
-
24This worked, but a couple of comments. First of all, I'm not sure why you escaped your backticks (if it's for the SO editor, you did it incorrectly). Secondly I'd recommend using ^dd$, just in case something else is running with the prefix dd. Finally, you don't need sudo to send the USR1 signal. Otherwise, good answer, +1. – gsgx Jul 14 '13 at 20:25
-
3@gsingh2011 For a description of why sudo is used and each command is placed as it is, read the article it's from (linked at the top of the answer) – James Jul 17 '13 at 23:17
-
I've added an answer below where I wrap
ddandpkillinto a function that can be called more easily than trying to juggle separate commands. – robru Apr 11 '14 at 00:43 -
3
-
27
-
@James, Hmm, but "making it output by prompting it with usr1" is not an intended use right? So would you say that this is actually just a hacky way of doing it? – Pacerier May 02 '15 at 12:33
-
@gsingh2011, Well there's no harm typing it again if
sudo kill -USR1 \pgrep dd`` doesn't work. – Pacerier May 02 '15 at 12:36 -
33@Speakus You have to use
kill -INFO $(pgrep ^dd$)on BSD systems (like OSX). – Torben Jun 06 '15 at 08:22 -
26
sudo pkill -usr1 ddis easier to remember, works perfectly fine (at least on Ubuntu 14.04), and is less to type. – Phizes Sep 07 '15 at 12:59 -
Usually this worked for me, but as I tried it now,
ddremained in process state D (uninterruptable sleep) and did not answer the kill until it finished. BS was way below file size, however. – Mitja Nov 29 '15 at 14:03 -
I think the output is not done by watch, but by dd itself. That means that if the dd line is executed in one terminal and the watch line in another, the result will not be what is expected. watch here is really just a loop with a clear screen, that by coincidence clears in sync with dd's output. – Penz Dec 15 '15 at 19:28
-
1I do
while true; do clean && pkill -usr1 dd && sleep 1; donebecause is much easier to read static text :V than using watch in that concrete case. Like that more than thepv. – m3nda May 05 '16 at 04:20 -
35I like this because I'm afraid
pvwill slow down the transfer, as TeddHansen showed it does. Also, I'll bet lots of people are Googling this because they already started theddoperation ;) – sudo Jul 07 '16 at 18:22 -
1
-
@James the linked site is (at least temporarily) down. To avoid link rot, please consider updating the answer to explain why sudo is necessary, or comment here? – Scott Stevens Jul 18 '16 at 08:14
-
@Phizes Bare
pkillis probably unsafe, especially with root. As somebody commented,sudois not needed here. Its safest to usekill -USR1 $pidbut a bit safer to usepkill -USR1 -nx dd. – akhan Oct 13 '16 at 18:40 -
This works on my system and it's a bit less to type:
watch -n 10 kill -USR1 $(pidof dd)– Antonello Nov 07 '16 at 11:01 -
@akhan Actually it wouldn't work on my system without root, which makes sense. Should you really be able to prod processes you don't own? Of course if dd is running as a user process, then the signal should be sent by the same user. Could you explain how it's unsafe? – Nobody Feb 25 '17 at 16:46
-
@Phizes Are you trying to kill a root process or process under another uid? Also, pkill can match any process that starts with dd, hence the
-nxflag (pgrep -l sshlists ssh-agent along with ssh). Signals can be sent to different uids and how the process handles them is platform specific. See here for relevant discussion for linux. – akhan Feb 26 '17 at 06:16 -
3
-
1
pgrepalone should not be recommended here, due to the way it matches substrings rather than the actual process name, and could unexpectedly send signals to other processes too. It would be better to usepgrep -x, orpidof, or just pass 'dd' directly topkill -xorkillall– mwfearnley Nov 11 '17 at 16:39 -
@sudo note that sending
SIGUSR1also affects the performance ofdd, as writing status info seems to happen in sync with (in the same thread as) the actual transfer; therefore any status writes triggered by the signal temporarily interrupt it. – Adrian Günter Apr 20 '18 at 20:19 -
No need to use
sudowithdd, you canchgrp floppy /dev/«device-that-you-will-write-to». Then if you are in groupfloppy, you can write to the device with less possibility of destroying stuff (double check thechgrp, before continuing). – ctrl-alt-delor Aug 04 '19 at 15:37 -
Answer by @Torben works like a charm in Mac Catalina as of March 2020.
– BhaveshDiwan Apr 30 '20 at 17:36sudo kill -INFO $(pgrep ^dd$) -
THIS NEEDS A WARNING! 2 days lost due to this command, then re-read the rest of the post to see there is an OSX option! Yes I should have read the whole answer, however, you should defo not provide a command that kills the process without a warning! – geedoubleya Apr 29 '22 at 09:57
-
1On FreeBSD (probably OSX too?) you can actually just press Ctrl+T to send SIGINFO
https://blog.danielisz.org/2018/06/21/the-power-of-ctrlt/
– Fsmv Jun 10 '22 at 00:20
A few handy sample usages with pv and less typing or more progress then other answers:
First you will need to install pv, with the command:
sudo apt-get install pv
Then some examples are:
pv -n /dev/urandom | dd of=/dev/null
pv -tpreb source.iso | dd of=/dev/BLABLA bs=4096 conv=notrunc,noerror
Note: the first sample is 5 characters less typing then dd if=/dev/urandom | pv | dd of=/dev/null.
And my favorite for cloning a disk drive (replace X with drive letters):
(pv -n /dev/sdX | dd of=/dev/sdX bs=128M conv=notrunc,noerror) 2>&1 | dialog --gauge "Running dd command (cloning), please wait..." 10 70 0
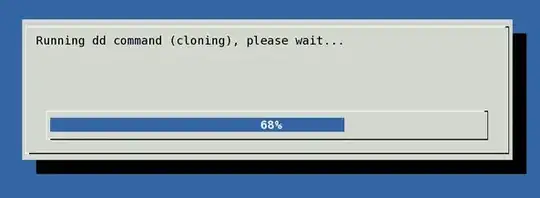
source: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-unix-dd-command-show-progress-while-coping/
Also for archiving myself.
-
3you will need to install also
dialogwith the commandapt-get install dialog– k7k0 Apr 29 '15 at 19:06 -
11
-
-
Calling from python? You may use it with "subprocess.Popoen". Despite not recommended because of security issues. Without graphicish results, this guy has made a similar impact: http://code.activestate.com/recipes/578907-python-awesome-dd/ Check out I guess. – JSBach Apr 30 '16 at 05:41
-
2
brew install pv dialogfor Mac. Also this gentleman computes with style. Bravo. – evilSnobu Apr 05 '18 at 13:18 -
-
On my system, when
pvis reading a file, it will read the entire file in one chunk, making the transfer jump to 100% and then you wait forddto finish writing the data. What fixed that for me was addingoflag=dsynctodd. So:(pv -tpreb file | dd of=/dev/sdX bs=1MB oflag=dsync conv=notrunc,noerror) 2>&1for console progress reporting and for the dialog progress bar(pv -n file | dd of=/dev/sdX bs=1MB oflag=dsync conv=notrunc,noerror) 2>&1 | dialog --gauge "Message..." 10 70 0. @zevero mentions the oflag in his answer. – omahena May 19 '22 at 13:07
For the sake of completeness:
Version 8.24 of the GNU coreutils includes a patch for dd introducing a parameter to print the progress.
The commit introducing this change has the comment:
dd: new status=progress level to print stats periodically
Many distributions, including Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS use this version.
- 966
- 6
- 6
-
just wanna add how I've compiled 8.24 coreutils:
apt install build-essentialandapt-get build-dep coreutils, then download coreutils-8.25.tar.xz,tar xvf coreutils-8.25.tar.xzconfigure --prefix=$HOME/usr/localand runmake. Newly compiledddwill be undersrcdir. You can copy it to /bin and replace existing one or jus run as src/dd – holms Aug 19 '16 at 22:37 -
3Cool! I like this feature. And it took just about 30 years to teach dd to print progress output. :-) – Johannes Overmann Apr 17 '17 at 09:34
-
2What a relief! I will immediately add this argument in a dd shell alias. – Stephan Henningsen May 31 '17 at 20:14
-
Note that the status will sometimes print with two numbers, one in SI units and the equivalent value in binary units (e.g.10 MB, 9.5 MiB). – palswim Sep 29 '17 at 19:29
-
... how periodically does it print stats? Because mine seems to print stats once, and then doesn't update until it's done. – CivMeierFan Jan 17 '24 at 18:31
Use Ctrl+Shift+T while dd is running, and it will output the progress (in bytes):
load: 1.51 cmd: dd 31215 uninterruptible 0.28u 3.67s
321121+0 records in
321120+0 records out
164413440 bytes transferred in 112.708791 secs (1458745 bytes/sec)
-
6Doesn't work for me on Kubuntu Trusty. Possibly conflicting key bindings? – jamadagni Nov 15 '14 at 04:33
-
15Great way. It works under OSX, but does not work under ubuntu 14.04 – Maxim Kholyavkin Nov 17 '14 at 06:39
-
1The first line is generated by the OS X, only the latter 3 lines are from
dd. – Itay Grudev Apr 01 '15 at 04:49 -
3
-
4This doesn't work on Ubuntu. Ctrl-T/Ctrl-Shift-T only output
^Tto the terminal (except many terminal apps will intercept Ctrl-Shift-T and open a new tab). Many searchers on OSX/BSD may appreciate this answer, but it should be made clear that it's not for Ubuntu (or GNU/LInux in general?) – mwfearnley Nov 11 '17 at 16:28 -
1
The best is using http://dcfldd.sourceforge.net/ it is easy to install through apt-get
- 627
-
3thanks for the pointer to dcfldd, very compatible with dd but some good new features. I especially like the standard progress. – Floyd Dec 20 '13 at 09:46
-
5
-
34
-
It has the options of
ddand optionstatus=onby default, for progress messages,statusinterval=N(N in blocks) for message update frequency andsizeprobe=[if|of]for a percentage indicator. I will alias it toDD:) – kavadias May 08 '18 at 17:09
Native progress status was added to dd!!!
The new version of Coreutils (8.24) adds a progress status to the dd tool:
Usage on Xubuntu 15.10:
Open a terminal and type these commands:
wget ftp://ftp.gnu.org/pub/gnu/coreutils/coreutils-8.24.tar.xz
tar -xf coreutils-8.24.tar.xz
cd coreutils-8.24
./configure && make -j $(nproc)
Run dd as root:
sudo su
cd src
./dd if=/dev/sdc of=/dev/sda conv=noerror status=progress
You will see: Bytes, seconds and speed (Bytes/second).
To check the versions of dd:
Native:
dd --version
New:
cd coreutils-8.24/src
./dd --version
- 421
If you have already started dd, and if you are writing a file such as when creating a copy of a pendrive to disk, you can use the watch command to constantly observe the size of the output file to see changes and estimate completion.
watch ls -l /pathtofile/filename
To see only file size (h-human view):
watch ls -sh /pathtofile/filename
- 197,895
- 55
- 485
- 740
- 8,375
-
-
4Useful, though this doesn't necessarily work if you're piping the dd output to something other than a file (eg gzip'ing before writing it to disk). – Ponkadoodle Jul 03 '14 at 03:32
-
The dd | pv | dd triad made my 50GB vm copy take 800 seconds, as opposed to 260 seconds using just dd. With this pipeline, at least, pv has no idea how big the input file is so it won't be able to tell you how far along you are so there's no disadvantage to doing it as follows- and you get a nice speed advantage:
I would avoid pv on anything large, and (if using Bash):
Control-Z the dd process
bg to put it in background. Observe that bg will give you output like [1] 6011 where the latter number is a process id. So, do:
while true; do kill -USR1 process_id ; sleep 5; done
where process_id is the process id you observed. Hit Control-C when you see something like:
[1]+ Done dd if=/path/file.qcow2 of=/dev/kvm/pxetest bs=4194304 conv=sparse
-bash: kill: (60111) - No such process
You are done.
Edit: Silly Systems Administrator! Automate your life, don't work! If I have a long dd process that I want to monitor, here's a one-liner that will take care of the whole enchilada for you; put this all on one line:
dd if=/path/to/bigimage of=/path/to/newimage conv=sparse bs=262144 & bgid=$!; while true; do sleep 1; kill -USR1 $bgid || break; sleep 4; done
You can, of course, script it, perhaps make $1 your input file and $2 your output file. This is left as an exercise for the reader. Note that you need that little sleep before the kill or the kill may die trying to send a signal to dd when it's not ready yet. Adjust your sleeps as desired (maybe even remove the second sleep altogether).
Bash- FTW! :-)
- 309
- 2
- 7
-
1
-
1@muru it depends. I don't know about your system but on CentOS7* the output is a little garbled; it's readable but does not look orderly. Also it stomps over your previous output so you lose history of the speed of your dd; mine varies between 20 MB/s and 300 MB/s. It's interesting to watch the numbers vary and instructive too. I think some of the large variance is due to LVM thin pools increasing the allocation for an LV I'm writing to. * yes this is an ubuntu forum but I got here looking for "dd monitor progress". It's the first result on Google. – Mike S May 07 '15 at 17:51
-
Oh, I meant in another terminal or screen window, run
sudo watch pkill dd. Then watchddoutput the stats comfortably. – muru May 07 '15 at 18:02 -
Won't pkill send SIGTERM by default? I don't even want to experiment, as pgrep dd comes up with 3 pid's when running a single dd: kthreadd, oddjob, and the dd. I'm afraid of what pkill will do. You could send the -USR1 signal with pkill but again I don't know if that's safe to send to the kernel thread or to obbjob. The watch command looks cleaner but it seems like a lot of extra steps just to avoid a while loop. Generally if I'm doing a dd in one window I'm going to do something right afterwards in the same shell. The while loop is safe: you know EXACTLY which pid gets the signal. – Mike S May 08 '15 at 14:01
-
mostly I don't care which pids get the signal, since I use
watch pkill -USR1 -x dd. Since I also usewatchfor other similar tasks, this one comes naturally. – muru May 08 '15 at 14:07 -
...I note that Robru's answer which uses a pkill should be safe, as it restricts the pkill to only the dd binary, using the
^dd$syntax. Update: Ah, -x. Ok that's better. – Mike S May 08 '15 at 14:07
http://linuxcommando.blogspot.com/2008/06/show-progress-during-dd-copy.html
Basically:
kill -USR1 < dd pid >
-
2"pkill -USR1 dd" is the simplest version I'm aware of (as long as you're just running one instance of dd, anyway). On my system I need sudo: "sudo pkill -USR1 dd". Works after you've typed the dd command, and you don't need to install anything new. – Fred Hamilton May 18 '15 at 18:49
On Ubuntu 16.04
Ubuntu 16.04 comes with dd (coreutils) Version 8.25 . Hence the option status=progress is Supported :-)
To use it, just add status=progress along with your dd command.
Example :
dd bs=4M if=/media/severus/tools-soft/OperatingSystems/ubuntu-16.04-desktop-amd64.iso of=/dev/null status=progress && sync
Gives the status as
1282846183 bytes (1.2 GiB, 1.1 GiB) copied, 14.03 s, 101.9 MB/s
- 9,866
Easiest is:
dd if=... of=... bs=4M status=progress oflag=dsync
oflag=dsync will keep your writing in sync, so information of status=progress is more accurate. However it might be a bit slower.
- 209
-
1according to https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/manual/html_node/dd-invocation.html , using
conv=fsyncis better – Chen Deng-Ta Jun 24 '17 at 12:49 -
Thanks for this! I'm doing dd to a remote lvm2 and the bs=4M increased my transfer by a factor of 20 and the progress indication is wonderful. – Lonnie Best Jan 19 '18 at 08:26
Use option status=progress to get the progress during the transfert.
In addition, conv=fsync will display I/O errors.
Example:
sudo dd if=mydistrib.iso of=/dev/sdb status=progress conv=fsync
- 296
This one forces dd to provide stats every 2 seconds which is default for watch:
watch killall -USR1 dd
To change from every 2 seconds to every 5 seconds, add -n 5 option like this:
watch -n 5 killall -USR1 dd
- 576
- 5
- 11
I really like ddrescue, it works as dd but gives output and doesn't fail on errors, on the contrary it has a very advanced algorithm an tries really hard to do a successful copy... There are also many GUIs for it
Project: https://www.gnu.org/software/ddrescue
Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ddrescue
- 1,653
Just in case anybody from CentOS land happens to find this thread...
The 'status=progress' option works with CentOS 7.5 and 7.6
The answer above by @davidDavidson implies the feature was newly added in Coreutils 8.24.
Version 8.24 of the GNU coreutils includes a patch for dd introducing a parameter to print the progress.
This may be the case, but CentOS might not be following the same versioning scheme.
The version of Coreutils that comes with CentOS 7.6.1810 is:
coreutils-8.22-23.el7.x86_64 : A set of basic GNU tools commonly used in shell scripts
And the version of dd that is installed is:
[root@hostname /]# dd --version
dd (coreutils) 8.22
Copyright (C) 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>.
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Written by Paul Rubin, David MacKenzie, and Stuart Kemp.
This shows versions 8.22.
However, I have tested the 'status=progress' with dd on both CentOS 7.5 and CentOS 7.6 (both with version 8.22 of Coreutils) and it functions properly.
I don't know why RedHat chooses to use such an old version of Coreutils but the functionality does exist with 8.22.
- 41
I have created bash wrapper over dd that will use pv to show progress. Put it into your .bashrc and use dd as usual:
# dd if=/dev/vvg0/root of=/dev/vvg1/root bs=4M
2GB 0:00:17 [ 120MB/s] [===========================================================>] 100%
0+16384 records in
0+16384 records out
2147483648 bytes (2.1 GB) copied, 18.3353 s, 117 MB/s
Source:
dd()
{
local dd=$(which dd); [ "$dd" ] || {
echo "'dd' is not installed!" >&2
return 1
}
local pv=$(which pv); [ "$pv" ] || {
echo "'pv' is not installed!" >&2
"$dd" "$@"
return $?
}
local arg arg2 infile
local -a args
for arg in "$@"
do
arg2=${arg#if=}
if [ "$arg2" != "$arg" ]
then
infile=$arg2
else
args[${#args[@]}]=$arg
fi
done
"$pv" -tpreb "$infile" | "$dd" "${args[@]}"
}
- 792
- 1
- 8
- 13
-
Good way but it does not work with commands like sudo or time. – Maxim Kholyavkin Nov 17 '14 at 07:28
-
1Put it into /usr/local/bin/dd with this on top:
#!/bin/bash. On bottom:tmp=":${PATH}:"; tmp=${tmp/:/usr/local/bin:/:}; tmp=${tmp%:}; PATH=${tmp#:}; dd "$@"Or you may wish to hardcodeddlocation. Then uselocal dd=/usr/bin/dd. Don't forget to add executable bit:chmod +x /usr/local/dd. – midenok Nov 19 '14 at 07:06
You can watch the progress of any coreutils program using progress - Coreutils Progress Viewer.
It can monitor:
cp mv dd tar cat rsync grep fgrep egrep cut sort md5sum sha1sum sha224sum sha256sum sha384sum sha512sum adb gzip gunzip bzip2 bunzip2 xz unxz lzma unlzma 7z 7za zcat bzcat lzcat split gpg
You can see the manpage
You can use it in a seperate terminal window while the command is running or launch it with the dd command:
dd if=/dev/sda of=file.img & progress -mp $!
Here & forks the first command and continues immediately instead of waiting until the command ends.
The progress command is launched with: -m so it waits until the monitored process ended, -p so it monitors a given pid and $! is the last command pid.
If you issue dd with sudo, you have to too with progress too:
sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=file.img &
sudo progress -m
# with no -p, this will wait for all coreutil commands to finish
# but $! will give the sudo command's pid
- 565
So today I got a little frustrated with trying to run kill in a loop while dd was running, and came up with this method for running them in parallel, easily:
function vdd {
sudo dd "$@" &
sudo sh -c "while pkill -10 ^dd$; do sleep 5; done"
}
Now just use vdd anywhere you'd normally use dd (it passes all arguments directly through) and you'll get a progress report printed every 5s.
The only downside is that the command doesn't return immediately when dd completes; so it's possible that this command can keep you waiting an extra 5s after dd returns before it notices and exits.
- 664
On my ubuntu 20.04 system I use, dcfldd
❯ sudo dcfldd if=20210708.img status=on of=/dev/sdd bs=1M sizeprobe=if
[46% of 3814Mb] 1792 blocks (1792Mb) written. 00:00:28 remaining.
Here in sizeprobe we have 3 options, if,of,BYTES which is to determine the size of the input,output or an amount of BYTES for use with status messages
status is by default 'on', I just used explicitly.
- 207
- 1
- 8
To add on @JSBack great answer, here is how you can get a dialog to wipe a disk with dd:
(dd if=/dev/zero | pv -s $(lsblk -b -o SIZE /dev/sdX | tail -n 1) -n | sudo dd of=/dev/sdX bs=1M) 2>&1 | dialog --gauge "Wiping disk /dev/sdX, Please wait..." 10 70 0
Some years ago, I got this dd progress script from somewhere (I do not recall where, and in my OPS infancy didn't include source or references in the code comments. Thanks to the original developer, and apologies for not having the source info):
#!/bin/bash
# show progress of dd command
# example: sdd.sh if=/dev/random of=random10M.dat bs=1M count=10
# script modified to redirect to stdout and show only units less than MB
unset parameters
ibs=512
obs=512
iconvrate=1024
oconvrate=1024
while [ -n "${1}" ] ; do
key="${1%%=}"
value="${1#=}"
case "${key}" in
(ibs) ibs="${value}" ;;
(obs) obs="${value}" ;;
(bs) ibs="${value}" ; obs="${value}" ;;
esac
parameters="${parameters} ${1}"
shift
done
BLOCKS and BYTES may be followed by the following multiplicative suffixes: xM M, c 1, w 2, b 512, kB 1000, K 1024, MB 1000*1000, M
10241024, GB 100010001000, G 10241024*1024, and so on for T, P, E, Z, Y.
case "${ibs: -1}" in
(c) ibs="${ibs%c}" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(w) ibs="$(( ${ibs%w} * 2))" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(b) ibs="${ibs%b}" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(B) ibs="${ibs%B}" ; iconvrate=1000 ;
case "${ibs: -1}" in
(K) ibs="$(( ${ibs%K} * 1000 ))" ;;
(M) ibs="$(( ${ibs%M} * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(G) ibs="$(( ${ibs%G} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(T) ibs="$(( ${ibs%T} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(P) ibs="$(( ${ibs%P} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(E) ibs="$(( ${ibs%E} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(Z) ibs="$(( ${ibs%Z} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(Y) ibs="$(( ${ibs%Y} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
esac ;;
(K) ibs="$(( ${ibs%K} * 1024 ))" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(M) ibs="$(( ${ibs%M} * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(G) ibs="$(( ${ibs%G} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(T) ibs="$(( ${ibs%T} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(P) ibs="$(( ${ibs%P} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(E) ibs="$(( ${ibs%E} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(Z) ibs="$(( ${ibs%Z} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
(Y) ibs="$(( ${ibs%Y} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; iconvrate=1024 ;;
esac
case "${obs: -1}" in
(c) obs="${obs%c}" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(w) obs="$(( ${obs%w} * 2))" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(b) obs="${obs%b}" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(B) obs="${obs%B}" ; oconvrate=1000 ;
case "${obs: -1}" in
(K) obs="$(( ${obs%K} * 1000 ))" ;;
(M) obs="$(( ${obs%M} * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(G) obs="$(( ${obs%G} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(T) obs="$(( ${obs%T} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(P) obs="$(( ${obs%P} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(E) obs="$(( ${obs%E} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(Z) obs="$(( ${obs%Z} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
(Y) obs="$(( ${obs%Y} * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 1000 ))" ;;
esac ;;
(K) obs="$(( ${obs%K} * 1024 ))" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(M) obs="$(( ${obs%M} * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(G) obs="$(( ${obs%G} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(T) obs="$(( ${obs%T} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(P) obs="$(( ${obs%P} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(E) obs="$(( ${obs%E} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(Z) obs="$(( ${obs%Z} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
(Y) obs="$(( ${obs%Y} * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 ))" ; oconvrate=1024 ;;
esac
tmp="$( mktemp )"
rm -f "${tmp}"
mkfifo "${tmp}"
chmod 0600 "${tmp}"
dd ${parameters} 2> ${tmp} &
pid=${!}
SECONDS=0
while [ -d /proc/${pid} ] ; do
sleep 1
kill -USR1 ${pid} > /dev/null 2> /dev/null
#114718+0 records in
#114717+0 records out
#58735104 bytes (59 MB) copied, 5.61526 seconds, 10.5 MB/s
read line1
read line2
read line3
isuff=""
osuff=""
ipssuff=""
opssuff=""
line1="${line1%+*}"
line2="${line2%+*}"
in="$(( ${line1} * ${ibs} ))"
out="$(( ${line2} * ${obs} ))"
ips="$(( ${in} / ${SECONDS} ))"
ops="$(( ${out} / ${SECONDS} ))"
for x in k M G T P E Z F ; do
for x in k M ; do
if [ ${ips} -gt ${iconvrate} ] ; then
ips="$(( ${ips} / ${iconvrate} ))"
ipssuff="${x}"
[ ${iconvrate} -eq 1000 ] && ipssuff="${ipssuff}B"
fi
if [ ${ops} -gt ${oconvrate} ] ; then
ops="$(( ${ops} / ${oconvrate} ))"
opssuff="${x}"
[ ${oconvrate} -eq 1000 ] && opssuff="${opssuff}B"
fi
if [ ${in} -gt ${iconvrate} ] ; then
in="$(( ${in} / ${iconvrate} ))"
isuff="${x}"
[ ${iconvrate} -eq 1000 ] && isuff="${ipssuff}B"
fi
if [ ${out} -gt ${oconvrate} ] ; then
out="$(( ${out} / ${oconvrate} ))"
osuff="${x}"
fi
done
echo -en "\rIn: ${in}${isuff} (${ips}${ipssuff}/sec) - Out: ${out}${osuff} (${ops}${opssuff}/sec)" > /dev/stderr
done < "${tmp}"
echo > /dev/stderr
rm -f "${tmp}"
This script starts dd and sends it a HUP signal each second, parsing the output to make it more readable and showing the progress data in a single updating line.
I didn't write the code and never took the time to optimize it.
- 300


dd if=/dev/zero bs=1M count=35000 | pv | dd of=VirtualDisk.raw. – Sopalajo de Arrierez Mar 28 '14 at 00:05pv bigfile.iso | dd of=VirtualDisk.raw bs=1M count=35000instead? – SiddharthaRT Oct 20 '14 at 12:10pv bigfile.iso | dd of=VirtualDisk.raw bs=1M count=35000works, verified. @SopalajodeArrierez, parameters can be given in the second dd. – SiddharthaRT Oct 20 '14 at 12:17pv < /dev/sda > /dev/sdbseems to get better speed (source) – Nicola Feltrin Feb 20 '15 at 13:30pvwhenkill -USR1works? (See answer by James) – Pacerier May 02 '15 at 12:39pv-method is approximately 40% slower than a directddwith a 5-secSIGUSR1. – Lars May 26 '15 at 08:09unable to locate package pv. – starbeamrainbowlabs Sep 09 '15 at 10:00pvstart reporting a much lower data rate compared tostatus=progressswitch for theddcommand? It appears that theddcommand has a slower decline in its data rate display, in my testpvwent down to 120 MB/s within in the first 10 GB, but at 43 GB, dd still shows 147 MB/s. – CMCDragonkai Nov 18 '15 at 09:14dd if=/dev/urandom | pv | of=/dev/sdbgives ~18MB/s write,dd if=/dev/zero | pv | of=/dev/sdbgives ~80MB/s, and plain olddd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdbgives ~550MB/s (close to SSD max write speed). All withbs=4096000. – Tedd Hansen May 07 '16 at 21:18sudo apt-add-repository universe; sudo apt-get updatein order to install pv. – mwfearnley May 14 '16 at 07:58pv. Maybe a CPU bottleneck? Was your CPU running full capacity due topv? – sudo Jul 07 '16 at 18:21status=progressis a huge and convenient time-saver. No need to install pv just to get progress any more. I'm so happy about that! :) It's a shame I can't upvote your answer twice. – Pabru Mar 08 '17 at 11:22O_DIRECT) should work, but your kernel and/orddmay not support it.status=progresswill select the speed and process of writing to the kernel cache, but the execution of thesyncto return the records to disk, we do not see https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/sysctl/vm.txt – Denis Denisov Apr 23 '17 at 00:55dd if=foo | pv | dd of=barvspv <foo >baris probably due to all of the copying of data: the data is read from devicefoointo the firstdd's memory space, then copied from there intopv's memory space using a 64K (on Linux at least) pipe buffer, then copied again into the seconddd's memory space using another 64K buffer, then finally written to devicebar– kbolino Aug 27 '17 at 19:40status, why didn't they enable it by default? – Damn Vegetables Jun 19 '18 at 19:18sudowithdd, you canchgrp floppy /dev/«device-that-you-will-write-to». Then if you are in group floppy, you can write to the device with less possibility of destroying stuff (double check thechgrp, before continuing). – ctrl-alt-delor Sep 22 '18 at 19:22.bashrcalong the lines ofalias dds='dd status=progress', then just useddsinstead ofdd. You could "overwrite" dd with an alias e.g.alias dd='dd status=progress'but that could be more dangerous (especially if you have any scripts that run dd and expect certain output!) – Doktor J Oct 01 '18 at 17:11pv file| dd of=deviceis slower because somehow it reads from the disk while writing? I wondered why writing is so slow using PV and saw that it READS a lot. Why? This is a 250 GB disk which sure has no 4k sectors! – JPT May 09 '20 at 09:15watch -n5 'cat /proc/meminfo | grep -i dirty'helped me get updated every 5 seconds about the amount of data that was left to be written to disk. SImple & perfect – Montmons Jan 05 '22 at 16:01status=progressseems to slow down significantly the copy operation; noticeable on slower devices like raspberry pi's – ccpizza Sep 19 '23 at 11:19