I need to reset the root password of my local mysql installation but it woudln't let me. I've tried this:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
* Stopping MySQL database server mysqld [ OK ]
[1]- Exit 1 sudo /usr/sbin/mysqld --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking
[2]+ Exit 1 sudo /usr/sbin/mysqld --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking
reg@regDesktopHome:~$ sudo mysqld --skip-grant-tables &
[1] 13651
reg@regDesktopHome:~$ 140627 19:02:02 [Warning] Using unique option prefix key_buffer instead of key_buffer_size is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use the full name instead.
reg@regDesktopHome:~$ mysql -u root mysql
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: NO)
reg@regDesktopHome:~$ sudo mysql -u root mysql
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: NO)
[1]+ Exit 1 sudo mysqld --skip-grant-tables
How can I get the password reset? edit 1 I got this:
$ ps ax| grep mysql
16515 ? Ssl 0:00 /usr/sbin/mysqld
16551 pts/23 S+ 0:00 grep --color=auto mysql
reg@regDesktopHome:~/semios/v3upgrade$ sudo kill -9 16515
reg@regDesktopHome:~/semios/v3upgrade$ ps ax| grep mysql
16678 ? Ssl 0:00 /usr/sbin/mysqld
16715 pts/23 S+ 0:00 grep --color=auto mysql
reg@regDesktopHome:~/semios/v3upgrade$ mysql -u root
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: NO)
looks like a process is automatically restarting mysql as soon as I kill it...
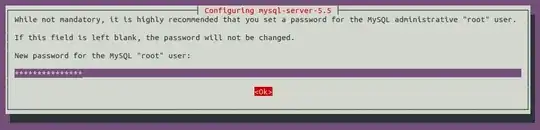
dpkg-reconfigure mariadb-server-10.1worked for MariaDB when all other solutions didn't. Thank you for this. – liviucmg Oct 03 '14 at 21:49dpkg-reconfigure mysql-server-5.5– Meetai.com Dec 29 '14 at 01:22dpkg-reconfiguredidn't prompt for password for me.. is there a way to force it? – Unirgy Dec 17 '15 at 18:02