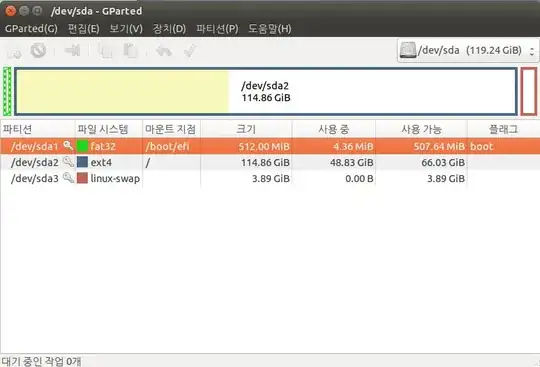
- Boot into a Ubuntu LiveUSB/CD.
- Open Gparted and shrink your
/dev/sda2/ to have enough space for the Windows installation.
- Create NTFS storage partition if necessary.
- Now restart and boot into a Windows installation media in UEFI mode.
Assuming that you have a UEFI based system, it would be better to install Windows to an unallocated disk partition. So the Windows installer could automate the creation of additional partitions such as EFI partition, recovery partition etc.
- Continue and follow the Windows installer until it is finished.
- Now boot back into a Ubuntu Live Media.
- Chroot into your old Linux file system as follows..
Mount your Linux root.
sudo mount /dev/sdaX /mnt/ (/dev/sda2 in your case)
Mount boot partition
sudo mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/boot
Bind these directories, so grub can find your Windows installation.
sudo mount –bind /dev /mnt/dev
sudo mount –bind /dev/pts /mnt/dev/pts
sudo mount –bind /proc /mnt/proc
sudo mount –bind /sys /mnt/sys
Then sudo chroot /mnt
If you successfully chrooted, then..
grub-install --efi-directory=/boot/efi /dev/sda
References: