How can I check my current Ubuntu version through the command-line and GUI?
4 Answers
As said in the official page, use:
lsb_release -a
Your version appears on the "Description" line. If you just want that line, type lsb_release -d.
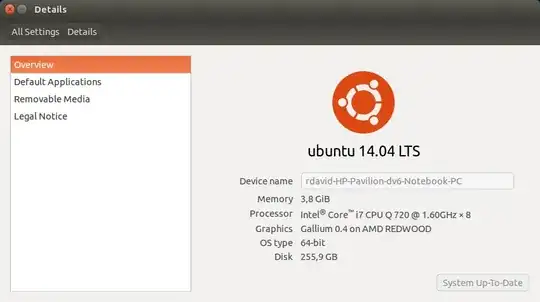
If you want to check it through your desktop environment, you can check System Settings → Details, which shows the data like this:
Alternatives are:
hostnamectlcat /etc/*ease
See a sample output of lsb_release, hostnamectl, and cat /etc/*ease calls:
$ lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS # <-- here
Release: 16.04
Codename: xenial
$ lsb_release -d
Description: Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS
$ hostnamectl
Static hostname: XXX
Icon name: computer-desktop
Chassis: desktop
Machine ID: 3d6dcfdd7b9f41dbb62b0e8cd75014ae
Boot ID: 4ff04a6baed54e719592f3255005a235
Operating System: Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS # <-- here
Kernel: Linux 4.10.0-38-generic
Architecture: x86-64
$ cat /etc/*ease
DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu
DISTRIB_RELEASE=16.04
DISTRIB_CODENAME=xenial
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS" # <--- here
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION="16.04.2 LTS (Xenial Xerus)"
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS"
VERSION_ID="16.04"
HOME_URL="http://www.ubuntu.com/"
SUPPORT_URL="http://help.ubuntu.com/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="http://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/"
VERSION_CODENAME=xenial
UBUNTU_CODENAME=xenial
- 10,069
-
83why is it this weird command? I can't ever remember it. Why not something like
os -v. Its sort of annoying. – Charlie Parker Dec 16 '16 at 07:07 -
6Seems like the 80's had a lot of good things, including simple and easy to remember UNIX commands! – João Rocha da Silva May 04 '17 at 11:01
-
12
-
1
-
31Ubuntu's official LTS Docker image (
ubuntu:xenial) does not havelsb_release; I had to parse/etc/os_releaseas noted in another answer. – Aaron D. Marasco Sep 16 '17 at 04:24 -
9@CharlieParker According to
man lsb_release, LSB stands for Linux Standard Base. – Serge Stroobandt Sep 18 '17 at 09:19 -
@CharlieParker Adding the following to your .bashrc:
export OS_CODE_NAME=$(lsb_release -cs); export OS_CODE_VERSION=$(lsb_release -rs)allows you do aenv | grep OS, which might be a bit more convenient. – spyle Nov 29 '17 at 23:05 -
-
3@CharlieParker
alias os="lsb_release -a". I agree this should be easier by default, but the beauty of UNIX is it allows you to fix stuff like this yourself without much of a fuss. – Austin Dean Jun 13 '18 at 14:57 -
This does not seem to be working in Ubuntu 18. In 16 it does (and in the docs you linked, it shows 14). – wordsforthewise May 14 '19 at 03:58
-
bash: lsb_release: command not foundandE: Unable to locate package lsb_releaseon Ubuntu 18 – techkuz Dec 18 '19 at 10:33 -
-
Code for ones which just needs short release description:
sb_release -d | grep -ioP ':\s+\K(.+?$)'– Agnius Vasiliauskas Oct 02 '20 at 08:45
Use:
cat /etc/*release
In my case it produced the following output:
DISTRIB_ID=LinuxMint
DISTRIB_RELEASE=17.2
DISTRIB_CODENAME=rafaela
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Linux Mint 17.2 Rafaela"
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION="14.04.3 LTS, Trusty Tahr"
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 14.04.3 LTS"
VERSION_ID="14.04"
HOME_URL="http://www.ubuntu.com/"
SUPPORT_URL="http://help.ubuntu.com/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="http://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/"
- 884
- 2,675
-
14
-
3On current mint releases
/etc/upstream-release/lsb-releasemight be of interest as well. – cheffo Apr 17 '17 at 19:26 -
12This works everywhere I tested. lsb_release doesn't work on all versions. for example in Ubuntu 16.04 on Docker. – Jay Jun 03 '17 at 07:11
-
3In my experience this is a more robust approach, some distributions will not have the lsb_release command – RutgerH Sep 27 '17 at 12:23
-
1
-
-
using command to get directly
grep 'CODENAME' /etc/lsb-release | cut -d'=' -f2– Larry Cai Oct 23 '18 at 12:16 -
1Good answer, as Ubuntu image installed from docker does not have lsb-release installed. – Binita Bharati Feb 04 '19 at 07:08
-
-
Use this in the terminal to show the details about the installed Ubuntu "version":
lsb_release -a
This may be more verbose than you need - maybe you just wanted to see 15.4? It can be shown separately by the option -r (--release):
$ lsb_release -r
Release: 15.04
Add -s (--short) for use in a script:
$ lsb_release -r -s
15.04
See the further examples for the more useful options -c (--codename) and -d (--description), and both combined:
$ lsb_release -c
Codename: vivid
$ lsb_release -d
Description: Ubuntu 15.04
$ lsb_release -dc
Description: Ubuntu 15.04
Codename: vivid
Note you can get similar information about the currently running kernel, and the hardware by the similar command:
$ uname -a
Linux mybox 3.19.0-31-generic #36-Ubuntu SMP Wed Oct 7 15:04:02 UTC 2015 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
- 13,065
- 5
- 49
- 65

/etc/apt/sources.listand seeing what repo it's pulling from. This was the only way I could figure out what Ubuntu image I was running inside of adocker run -it --rmwhich apparently doesn't installlsb_release– Bratchley Nov 07 '17 at 16:10