The aim:
You want a nice little MAC changer which you can just call using a keyboard shortcut and feed it a MAC? It should also be able to read it from the clipboard?
Here is what you want:
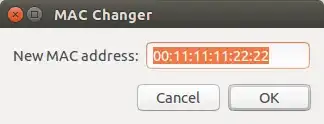
Preparation:
To access the clipboard, we need xsel. Install it with the command
sudo apt-get install xsel
The scripts:
We need to make four little shell scripts to do your work.
Create the following files in /usr/local/bin using your favourite plain text editor. You will need sudo/root privileges to save them in the desired location.
get-mac:
#! /bin/bash
ip addr show eth0 | awk '/ether/{print $2}'
get-mac-dialog:
#! /bin/bash
zenity --info --title "MAC Changer" --text "Current MAC address: $(get-mac)" 2>/dev/null
change-mac:
#! /bin/bash
ifconfig eth0 down &&
ifconfig eth0 hw ether "$@" || exit 1
ifconfig eth0 up
change-mac-dialog:
#! /bin/bash
oldmac=$(get-mac)
newmac=$(zenity --entry --title "MAC Changer" --text "New MAC address:" --entry-text $oldmac 2>/dev/null) &&
gksudo change-mac $newmac || zenity --error --title "MAC Changer" --text "Failed to change MAC address"
paste-mac:
#! /bin/bash
gksudo change-mac $(xsel -ob)
If your network interface has any other name than eth0, you must replace all 4 occurrences of it in the scripts with the real name!
Now set the correct ownerships and permissions:
chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/get-mac /usr/local/bin/get-mac-dialog /usr/local/bin/change-mac /usr/local/bin/change-mac-dialog /usr/local/bin/paste-mac
sudo chown root: /usr/local/bin/get-mac /usr/local/bin/get-mac-dialog /usr/local/bin/change-mac /usr/local/bin/change-mac-dialog /usr/local/bin/paste-mac
Usage summary:
get-mac:
Simply print the current MAC address of eth0 to the terminal.
get-mac-dialog:
Show a small dialog window displaying the current MAC address of eth0.
change-mac:
Directly try to change the MAC address of eth0. It will disconnect and reconnect the interface to do this. You must run this as root!
Example: sudo change-mac 12:34:56:78:9a:bc
change-mac-dialog:
Show a nice little GUI prompt asking you to enter the new MAC address (default text is the current MAC). You will be prompted for a sudo password using the GUI gksudo.
paste-mac:
Call gksudo change-mac with the current clipboard content as argument. You will be prompted for a sudo password using the GUI gksudo.
Shortcuts:
I assume you can create custom shortcuts for scripts yourself, otherwise please refer here.
Note that you should probably not create a shortcut for change-mac (needs to run as root and needs a MAC as argument) or get-mac (prints output to terminal). Use change-mac-dialog and get-mac-dialog as GUI replacement for them. paste-mac does neither need any input nor does it create output, so you can make a shortcut for that without any problem.
