I had a Windows 8.1 and Ubuntu (probably the latest version) dual boot. I decided to delete the Ubuntu OS and proceeded to delete the Ubuntu disk partition. I then deleted the Linux boot loader. However when I access the boot menu of my computer I still find the Ubuntu options. So I suspect that some of the Ubuntu memory partitions in my Disk Management are still intact.
Here is a picture of the view in my Disk Management before I deleted the 30.00 GB Healthy (Primary Partition) which I know was definitely Ubuntu.
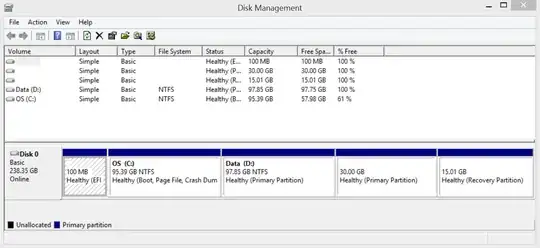
I now suspect that the 15.01 GB Healthy (Recovery Partition) might also be Ubuntu but the 100 MB Healthy (EFI System Partition) is a mystery to me. When right-cliking either one I only get the option "Help" but not "Delete".
Which partitions are Ubuntu and how can I be sure before deleting them?