< Observing the Sky from 30°S
 Observing the Sky from 30°S
Observing the Sky from 30°S 
Introduction · Sky maps · Tables · Selected areas of sky · Sources and references

Introduction · Sky maps · Tables · Selected areas of sky · Sources and references
The tables below make use of the following symbols:
![]()
![]()
![]()
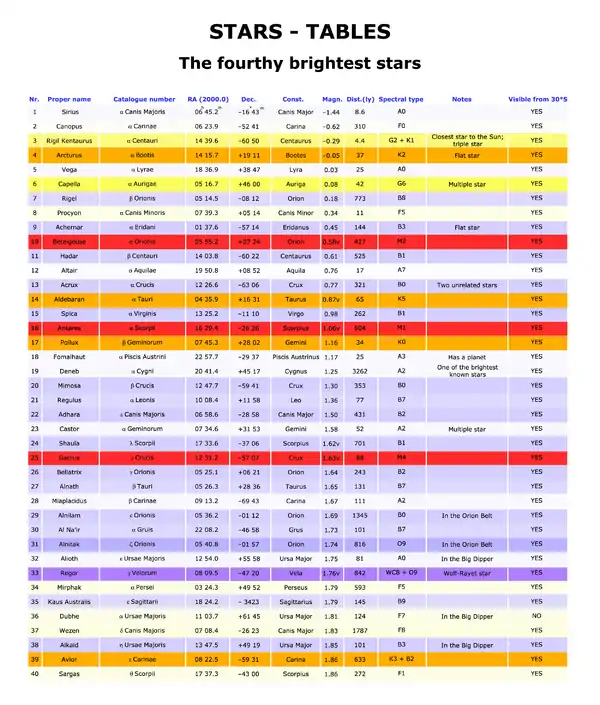
The 40 brightest stars
Column Headings
- Proper name: the name of the star.
- Catalogue number: the Bayer designation of the star, a system developed by Henry Draper in 1603.
- RA(2000.0) and Dec.: right ascension and declination, referred to the 2000.0 equinox.
- Const.: the constellation in which the star is located.
- Magn.: the apparent magnitude of the star.
- Dist.(ly): approximate distance of the star, expressed in light-years.
- Spectral type: the spectral class, the luminosity class and peculiarity.
- Notes: notable notes about the star.

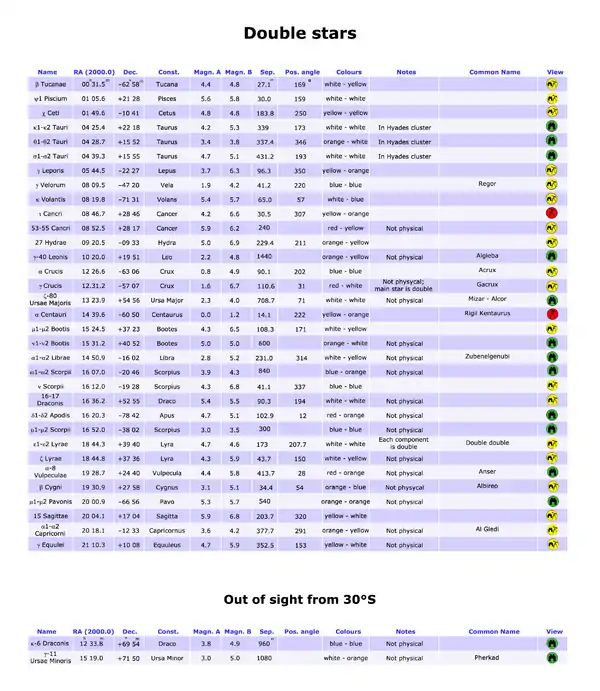
Double stars
Column Headings
- Name: the Bayer or Flamsteed designation of the star.
- RA(2000.0) and Dec.: right ascension and declination, referred to the 2000.0 equinox.
- Const.: the constellation in wich the star is located.
- Mag. A: the apparent magnitude of the primary component.
- Mag. B: the apparent magnitude of the secondary component.
- Sep.: the separation between the components, expressed in seconds of arc.
- Pos. angle: the position angle, counted in degrees from north (0°) through east (90°), south (180°), and west (270°). The position angles are for the component B with respect to the component A.
- Colours: the colours of the two components of the system, based on their spectral type.
- Notes: notable notes about the star system, membership in star clusters, physic of the system.
- Common name: the proper name of the star system.

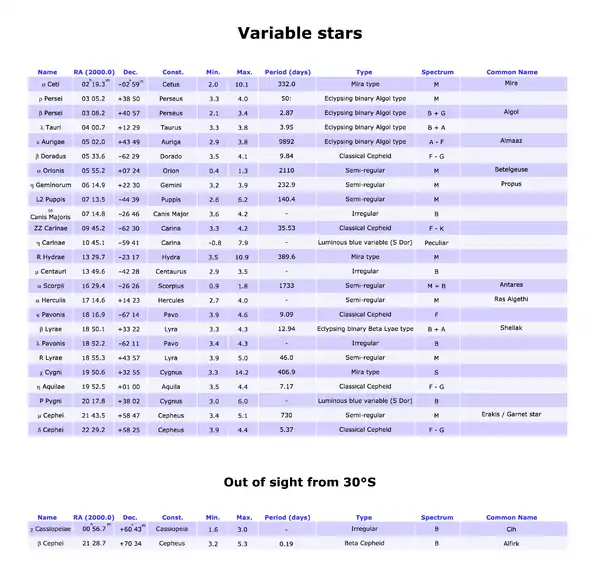
Variable stars
Column Headings
- Name: the Bayer, Flamsteed or variable designation of the star.
- RA(2000.0) and Dec.: right ascension and declination, referred to the 2000.0 equinox.
- Const.: the constellation in wich the star is located.
- Min.: the apparent magnitude at maximum brightness.
- Max.: the apparent magnitude at minimum brightness.
- Period (days): the average period of variation in days.
- Type: the type of variability.
- Spectrum: the spectral class of the star. In eclypsing binaries, the spectra of both the components are indicated; in pulsating variables, the variation of the spectrum is showed.
- Common name: the proper name of the star.

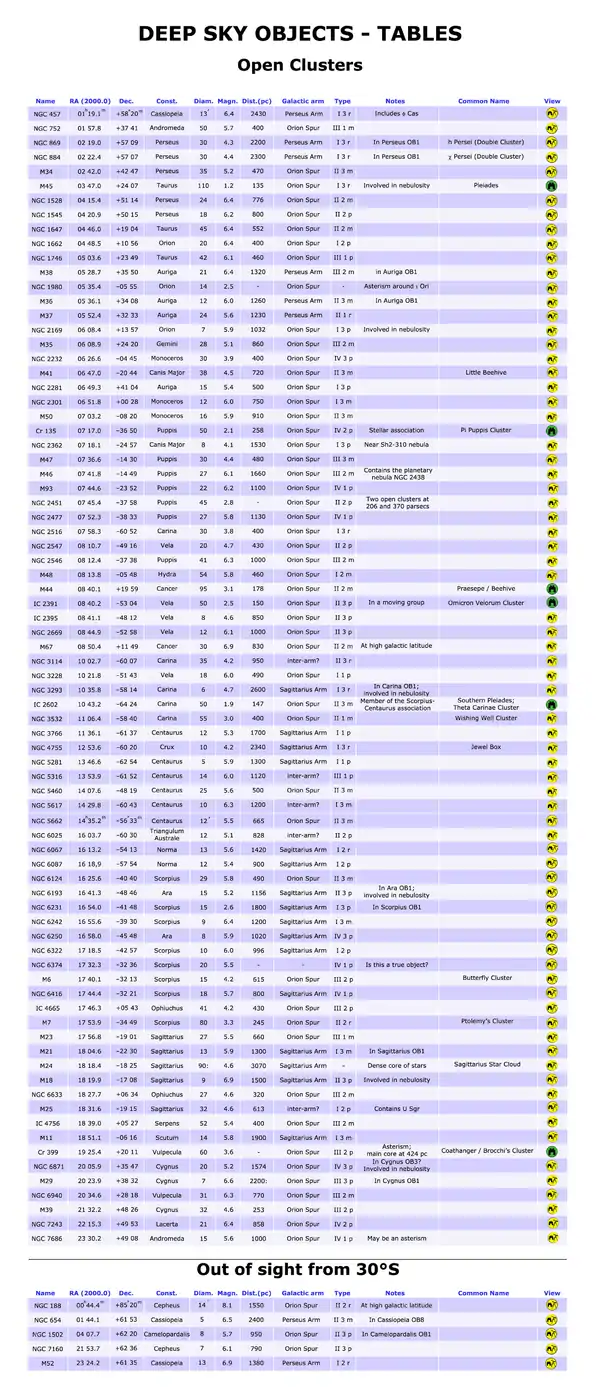
Open clusters
Column Headings
- Name: the cluster’s name as plotted on the maps.
- RA(2000.0) and Dec.: right ascension and declination, referred to the 2000.0 equinox.
- Const.: the constellation in which the cluster is located.
- Diam.: apparent diameter expressed in minutes of arc.
- Magn.: the apparent magnitude of the cluster; a symbol “:” after this value means an approximation.
- Dist.(pc): approximate distance of the cluster, expressed in parsec. To obtain the distance in light-years, multiply for 3.26.
- Galactic arm: the spiral arm of the Milky Way in wich the cluster is located.
- Type: descriptive type based on the system developed by R. J. Trumpler in 1930. It is composed by three parts:
- Concentration
- I. Detachted; strong concentration toward centre.
- II. Detachted; weak concentration toward centre.
- III. Detachted; no concentration toward centre.
- IV. Not well detachted from surrounding star field.
- Range in brightness
- 1. Small range in brightness.
- 2. Moderate range in brightness.
- 3. Large range in brightness.
- Richness
- p Poor (less than 50 stars).
- m Moderately rich (50 to 100 stars).
- r Rich (more than 100 stars).
- Concentration
- Notes: notable notes about the cluster, membership in OB associations, nebulosity.
- Common name: the proper name of the cluster.

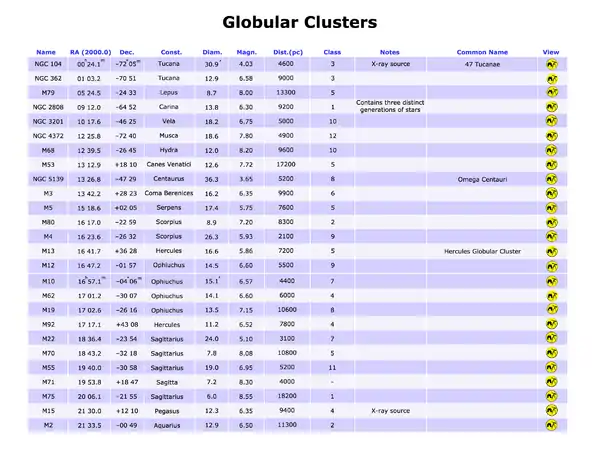
Globular clusters
Column Headings
- Name: the cluster’s name as plotted on the maps.
- RA(2000.0) and Dec.: right ascension and declination, referred to the 2000.0 equinox.
- Const.: the constellation in which the cluster is located.
- Diam.: apparent diameter expressed in minutes of arc.
- Magn.: the apparent magnitude of the cluster; a symbol “:” after this value means an approximation.
- Dist.(pc): approximate distance of the cluster, expressed in parsec. To obtain the distance in light-years, multiply for 3.26.
- Class: concentration class of the globular cluster based on the system developed by H. Shapley in 1927. The values range from 1 to 12; the smaller is the number, the higher is the concentration of stars toward the centre of the cluster.
- Notes: notable notes about the cluster, strong X-ray sources.
- Common name: the proper name of the cluster.

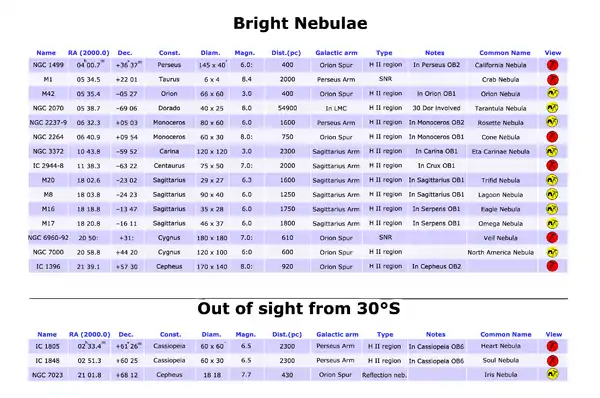
Bright nebulae
Column Headings
- Name: the nebula’s name as plotted on the maps.
- RA(2000.0) and Dec.: right ascension and declination, referred to the 2000.0 equinox.
- Const.: the constellation in which the nebula is located.
- Diam.: apparent diameter expressed in minutes of arc.
- Magn.: the apparent magnitude of the nebula; a symbol “:” after this value means an approximation.
- Dist.(pc): approximate distance of the nebula, expressed in parsec. To obtain the distance in light-years, multiply for 3.26.
- Galactic arm: the spiral arm of the Milky Way in which the nebula is located.
- Type: the type of the nebula:
- H II regions are nebulae with an high rate of ionized hydrogen emitting light.
- Reflection nebulae are clouds of gas and dust illuminated by a nearby star.
- SNR is a supernova remnant, a bubble of filamentary gas expelled after the explosion of a supernova.
- Notes: notable notes about the nebula, membership in OB associations.
- Common name: the proper name of the nebula.

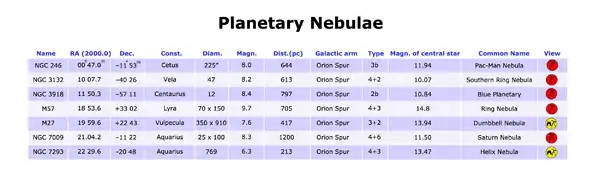
Planetary nebulae
Column Headings
- Name: the nebula’s name as plotted on the maps.
- RA(2000.0) and Dec.: right ascension and declination, referred to the 2000.0 equinox.
- Const.: the constellation in which the nebula is located.
- Diam.: apparent diameter expressed in seconds of arc.
- Magn.: the apparent magnitude of the nebula; a symbol “:” after this value means an approximation.
- Dist.(pc): approximate distance of the nebula, expressed in parsec. To obtain the distance in light-years, multiply for 3.26.
- Galactic arm: the spiral arm of the Milky Way in which the nebula is located.
- Type: the aspect of the nebula, according to the Vorontsov-Velyaminon system:
- 1. Stellar image.
- 2. Smooth disk (a, brighter toward the centre; b, uniform brightness; c, traces of ring structure).
- 3. Irregular disk (a, very irregular brightness distribution; b, traces of ring structure).
- 4. Ring structure.
- 5. Irregular form (similar to a diffuse nebula).
- 6. Anomalous form.
- Magn. of the central star: the apparent magnitude of the star that originates the nebula.
- Common name: the proper name of the nebula.

Galaxies
Column Headings
- Name: the galaxy’s name as plotted on the maps.
- RA(2000.0) and Dec.: right ascension and declination, referred to the 2000.0 equinox.
- Const.: the constellation in which the galaxy is located.
- Diam.: apparent diameter expressed in minutes of arc.
- Magn.: the apparent magnitude of the galaxy; a symbol “:” after this value means an approximation.
- Dist.(Mpc): approximate distance of the galaxy, expressed in megaparsec (millions of parsec). To obtain the distance in light-years, multiply *for 3,260,000.
- Type: the Hubble type of the galaxy, as described in the introduction.
- Nuclear class: the nuclear class according to the system developed by G. de Vancouleurs in 1976; numbers from 1 to 5 indicates the increasing *of the luminosity of the nucleus.
- Common name: the proper name of the galaxy.

This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.