Road signs in North Macedonia are regulated in Правилник за сообраќајните знаци, опрема и сигнализација на патот / Pravilnik za soobraḱajnite znaci, oprema i signalizacija na patot.[1]
The road signs in North Macedonia follow the 1968 Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, and the former Yugoslav standard road signs, used by the successor states of SFR Yugoslavia. North Macedonia adopted its own road sign standard after the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia gained its independence from Yugoslavia in the early 1990s. Inscriptions on road signs can be both in Cyrillic and Latin, as well as in Albanian. The SNV typeface and Arial Bold typeface are used on Macedonian road signs as well as in other former Yugoslav states, Bulgaria and Romania. In Switzerland, the SNV typeface was also used on road signs before being replaced with the ASTRA-Frutiger typeface in 2003.
The former Yugoslavia had originally signed the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals on November 8, 1968 and ratified it on June 6, 1977.[2] Yugoslavia formerly used a yellow background on warning signs. After the breakup of Yugoslavia when the Republic of Macedonia declared its independence in 1991, the country succeeded to the Vienna Convention on December 20, 1999 (initially under the name Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia,[3] but since 2019 under the name North Macedonia after the long-term dispute over the name of the Republic of Macedonia between Greece and the former Yugoslav Republic was resolved by renaming the latter one to North Macedonia).
Warning signs
 Other hazards
Other hazards Curve to left
Curve to left Curve to right
Curve to right Double curve, first to the left
Double curve, first to the left Double curve, first to the right
Double curve, first to the right Steep downhill
Steep downhill Steep uphill
Steep uphill Uneven road
Uneven road Warning for bumps
Warning for bumps Dip
Dip Be careful in winter
Be careful in winter Slippery road
Slippery road Rockfall on the left
Rockfall on the left Rockfall on the right
Rockfall on the right Loose gravel
Loose gravel Crosswind on the left
Crosswind on the left Crosswind on the right
Crosswind on the right Road narrows
Road narrows Road narrows on the right
Road narrows on the right Road narrows on the left
Road narrows on the left Roadworks
Roadworks Traffic queues likely
Traffic queues likely End of dual carriageway
End of dual carriageway Two-way traffic
Two-way traffic Mobile bridge
Mobile bridge Quayside or riverbank
Quayside or riverbank Traffic lights
Traffic lights Traffic lights
Traffic lights Pedestrians ahead
Pedestrians ahead Pedestrian crossing
Pedestrian crossing Children
Children Cyclists
Cyclists Domestic animals
Domestic animals Wild animals
Wild animals Low aircraft
Low aircraft Buses ahead
Buses ahead Tramway
Tramway Roundabout
Roundabout Roiling or slipping vehicle
Roiling or slipping vehicle Soft verges
Soft verges Tunnel
Tunnel Warning of fire
Warning of fire Level crossing with barrier ahead
Level crossing with barrier ahead Level crossing without barrier ahead
Level crossing without barrier ahead Single track level crossing
Single track level crossing Multi-track level crossing
Multi-track level crossing Distance of level crossing with barrier
Distance of level crossing with barrier Distance of level crossing without barrier
Distance of level crossing without barrier
Prohibitory signs
 Give way
Give way Stop
Stop Priority for oncoming traffic
Priority for oncoming traffic All vehicles prohibited in both directions
All vehicles prohibited in both directions No entry
No entry No cars
No cars No bus
No bus No trucks
No trucks No vehicles carrying dangerous water pollutants
No vehicles carrying dangerous water pollutants No vehicles carrying explosives
No vehicles carrying explosives No vehicles carrying dangerous goods
No vehicles carrying dangerous goods No trailers
No trailers No articulated vehicles
No articulated vehicles No tractors
No tractors No motorcycles
No motorcycles No mopeds
No mopeds No bike
No bike No animal-drawn vehicles
No animal-drawn vehicles No equestrians
No equestrians No handcarts
No handcarts No pedestrians
No pedestrians No motor vehicles
No motor vehicles No motor and animal-drawn vehicles
No motor and animal-drawn vehicles Maximum width
Maximum width Maximum height
Maximum height Maximum weight
Maximum weight Maximum weight per axle
Maximum weight per axle Maximum length
Maximum length Minimum safe distance
Minimum safe distance No left turn
No left turn No right turn
No right turn No u-turn
No u-turn No overtaking
No overtaking No overtaking by trucks
No overtaking by trucks Maximum speed 10 km
Maximum speed 10 km Maximum speed 20 km
Maximum speed 20 km Maximum speed 30 km
Maximum speed 30 km Maximum speed 40 km
Maximum speed 40 km Maximum speed 50 km
Maximum speed 50 km Maximum speed 60 km
Maximum speed 60 km Maximum speed 70 km
Maximum speed 70 km Maximum speed 80 km
Maximum speed 80 km Maximum speed 90 km
Maximum speed 90 km Maximum speed 100 km
Maximum speed 100 km Maximum speed 110 km
Maximum speed 110 km Maximum speed 120 km
Maximum speed 120 km Maximum speed 130 km
Maximum speed 130 km No stopping
No stopping No parking
No parking No parking in odd days
No parking in odd days No parking in even days
No parking in even days Customs
Customs Police
Police Toll
Toll No use horns
No use horns No photography
No photography
Mandatory signs
 Proceed straight
Proceed straight Turn left ahead
Turn left ahead Turn right ahead
Turn right ahead Turn left
Turn left Turn right
Turn right U-turn
U-turn Turn left or right
Turn left or right Proceed straight or turn left
Proceed straight or turn left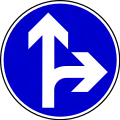 Proceed straight or turn right
Proceed straight or turn right Roundabout
Roundabout Pass onto left
Pass onto left Pass onto right
Pass onto right Bike path
Bike path Equestrian path
Equestrian path Pedestrian path
Pedestrian path Pedestrian and bike path
Pedestrian and bike path Pedestrian and bike path
Pedestrian and bike path Snow chains mandatory
Snow chains mandatory Minimum speed limit
Minimum speed limit Pass either side
Pass either side
References
- ↑ "Дејуре, платформа за консолидирање на закони". dejure.mk. Retrieved 2023-02-28.
- ↑ "United Nations Treaty Collection". treaties.un.org. Retrieved 2023-12-08.
- ↑ "Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals - unece" (PDF). United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). UNITED NATIONS. p. 154. Retrieved 2023-12-22.