< WikiJournal of Science
WikiJournal of Science/Volume 5 Issue 1
WikiJournal of Science
Open access • Publication charge free • Public peer review • Wikipedia-integrated
Journal issues
Current
Previous
Volume 1(1)
Volume 1(2)
Volume 2(1)
Volume 3(1)
Volume 4(1)
Volume 5(1)
Volume 6(1)
|
VOLUME 5 (2022)
ISSUE 1
Previous issue
Authors: Michel Bakni, Sandra Hanbo
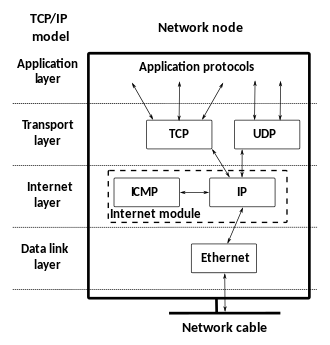
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is an internetwork protocol that is active at the internet layer according to the TCP/IP model, it was developed in 1981 within a project managed by Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. In the following years, the use of IPv4 grew to dominate data networks around the world, becoming the backbone of the modern Internet. In this survey, we highlight the operation of the protocol, explain its header structure, and show how it provides the following functions: Quality of service control, host addressing, data packet fragmentation and reassembly, connection multiplexing, and source routing. Furthermore, we handle both address-related and fragmentation-related implementation problems, focusing on the IPv4 address space exhaustion and explaining the short and long terms proposed solutions. Finally, this survey highlights several auxiliary protocols that provide solutions to IPV, namely address resolution, error reporting, multicast management, and security.
doi: 10.15347/WJS/2022.002
Authors: William Lytle, Chelsea Schelly, Matthew Kelly, Mark Rudnicki, Zoe Ketola
This study examines the existing social license of the forest products industry in a rural community in Michigan, located in the northern midwestern United States. This is accomplished through a series of interviews with industry and community stakeholders, aimed at understanding how they view social license and its impacts. Perceptions of natural resource management and community relations are highly related to the community's history with industries, relationships with place, and perspectives on what work is of value. The results suggest that social license varies spatially, and it is the place-based context that allows local industry to have a higher degree of license than non-local industry actors. Thus, social license is spatially contingent, based on particular socio-spatial and historical contexts. In this paper, we articulate how this spatial and historical contextualization shapes perceptions of acceptable operating practices. This paper offers refinement of the concept of social license while also considering how natural resource based industries can successfully meet evolving management challenges when their social license may be vulnerable to disturbances. Having an adequate social license is an undeniable asset for industry, while an inadequate social license is a liability. Stakeholders have the ability to damage or halt industry operations, often with just cause in the face of natural resource extraction and exploitation. Our evaluation of social licenses intends to shed light on the conditions that precipitate such conflicts.
doi: 10.15347/WJS/2022.001
|
WikiJournal of Science
www.WikiJSci.org On social media
|
This article is issued from Wikiversity. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.