The SATA hdd is connected with a USB adapter cable.
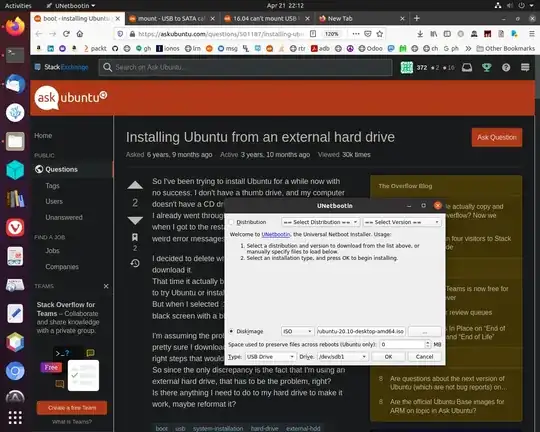
How is unetbootin used to write an ISO image:
to an external hard drive for installing Ubuntu?
It's not clear that unetbootin is listing the external hard drive, which is connected from a USB to SATA adapter, as a USB type media.
(parted)
(parted) print devices
/dev/sda (1000GB)
/dev/sdb (360GB)
/dev/mapper/vgubuntu-swap_1 (1023MB)
/dev/mapper/vgubuntu-root (999GB)
(parted)
(parted) q
nicholas@mordor:~$
nicholas@mordor:~$ sudo fdisk -l
Disk /dev/loop0: 138.81 MiB, 145534976 bytes, 284248 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop1: 150.4 MiB, 157327360 bytes, 307280 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop2: 138.92 MiB, 145645568 bytes, 284464 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop3: 150.1 MiB, 157298688 bytes, 307224 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop4: 99.22 MiB, 104030208 bytes, 203184 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop5: 99.15 MiB, 103964672 bytes, 203056 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop6: 55.48 MiB, 58159104 bytes, 113592 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop7: 55.46 MiB, 58142720 bytes, 113560 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/sda: 931.53 GiB, 1000204886016 bytes, 1953525168 sectors
Disk model: WDC WD10EADS-00P
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x8b0be982
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sda1 * 2048 1050623 1048576 512M b W95 FAT32
/dev/sda2 1052670 1953523711 1952471042 931G 5 Extended
/dev/sda5 1052672 1953523711 1952471040 931G 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/mapper/vgubuntu-root: 930.6 GiB, 998638616576 bytes, 1950466048 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/vgubuntu-swap_1: 976 MiB, 1023410176 bytes, 1998848 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop8: 125.87 MiB, 131960832 bytes, 257736 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop9: 131.61 MiB, 137990144 bytes, 269512 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop10: 105.88 MiB, 111001600 bytes, 216800 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop11: 128.27 MiB, 134492160 bytes, 262680 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop12: 162.89 MiB, 170778624 bytes, 333552 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop13: 217.92 MiB, 228478976 bytes, 446248 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop14: 218.102 MiB, 229629952 bytes, 448496 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop15: 64.36 MiB, 67477504 bytes, 131792 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop16: 64.79 MiB, 67915776 bytes, 132648 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop17: 101.101 MiB, 106938368 bytes, 208864 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop18: 19.9 MiB, 20840448 bytes, 40704 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop19: 462.59 MiB, 485044224 bytes, 947352 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop20: 470.51 MiB, 493355008 bytes, 963584 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop21: 65.32 MiB, 68489216 bytes, 133768 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop22: 65.31 MiB, 68476928 bytes, 133744 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop23: 29.16 MiB, 30568448 bytes, 59704 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop24: 29.28 MiB, 30695424 bytes, 59952 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop25: 51.2 MiB, 53501952 bytes, 104496 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop26: 51.4 MiB, 53522432 bytes, 104536 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop27: 32.28 MiB, 33841152 bytes, 66096 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop28: 32.28 MiB, 33841152 bytes, 66096 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/sdb: 335.36 GiB, 360080694272 bytes, 703282606 sectors
Disk model: Storage Device
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xa4c751ab
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdb1 * 2048 694882303 694880256 331.4G 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 694884350 703281151 8396802 4G 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 694884352 703281151 8396800 4G 82 Linux swap / Solaris
nicholas@mordor:~$
nicholas@mordor:~$ mount
sysfs on /sys type sysfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)
proc on /proc type proc (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)
udev on /dev type devtmpfs (rw,nosuid,noexec,relatime,size=3973980k,nr_inodes=993495,mode=755)
devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,nosuid,noexec,relatime,gid=5,mode=620,ptmxmode=000)
tmpfs on /run type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,size=801120k,mode=755)
/dev/mapper/vgubuntu-root on / type ext4 (rw,relatime,errors=remount-ro)
securityfs on /sys/kernel/security type securityfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)
tmpfs on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev)
tmpfs on /run/lock type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,size=5120k)
tmpfs on /sys/fs/cgroup type tmpfs (ro,nosuid,nodev,noexec,mode=755)
cgroup2 on /sys/fs/cgroup/unified type cgroup2 (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,nsdelegate)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/systemd type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,xattr,name=systemd)
pstore on /sys/fs/pstore type pstore (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)
none on /sys/fs/bpf type bpf (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,mode=700)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/rdma type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,rdma)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu,cpuacct type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,cpu,cpuacct)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/pids type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,pids)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/memory type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,memory)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/blkio type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,blkio)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/freezer type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,freezer)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/net_cls,net_prio type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,net_cls,net_prio)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/hugetlb type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,hugetlb)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/perf_event type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,perf_event)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,cpuset)
cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/devices type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,devices)
systemd-1 on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type autofs (rw,relatime,fd=28,pgrp=1,timeout=0,minproto=5,maxproto=5,direct,pipe_ino=16508)
debugfs on /sys/kernel/debug type debugfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)
mqueue on /dev/mqueue type mqueue (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)
tracefs on /sys/kernel/tracing type tracefs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)
hugetlbfs on /dev/hugepages type hugetlbfs (rw,relatime,pagesize=2M)
fusectl on /sys/fs/fuse/connections type fusectl (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)
configfs on /sys/kernel/config type configfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/chromium_1557.snap on /snap/chromium/1557 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/chromium_1558.snap on /snap/chromium/1558 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/codium_157.snap on /snap/codium/157 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/codium_162.snap on /snap/codium/162 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/core_10908.snap on /snap/core/10908 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/core_10958.snap on /snap/core/10958 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/core18_1997.snap on /snap/core18/1997 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/docker_471.snap on /snap/docker/471 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/docker_796.snap on /snap/docker/796 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/electrum_2.snap on /snap/electrum/2 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/geth_477.snap on /snap/geth/477 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/gnome-3-28-1804_145.snap on /snap/gnome-3-28-1804/145 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/core18_1988.snap on /snap/core18/1988 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/gnome-3-34-1804_60.snap on /snap/gnome-3-34-1804/60 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/gnome-3-34-1804_66.snap on /snap/gnome-3-34-1804/66 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/gtk-common-themes_1513.snap on /snap/gtk-common-themes/1513 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/gtk-common-themes_1514.snap on /snap/gtk-common-themes/1514 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/ipfs-desktop_24.snap on /snap/ipfs-desktop/24 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/libxml2_69.snap on /snap/libxml2/69 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/netbeans_41.snap on /snap/netbeans/41 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/netbeans_45.snap on /snap/netbeans/45 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/powershell_160.snap on /snap/powershell/160 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/ruby_201.snap on /snap/ruby/201 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/ruby_212.snap on /snap/ruby/212 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/snap-store_498.snap on /snap/snap-store/498 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/powershell_158.snap on /snap/powershell/158 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/snap-store_518.snap on /snap/snap-store/518 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/snapd_11402.snap on /snap/snapd/11402 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/var/lib/snapd/snaps/snapd_11588.snap on /snap/snapd/11588 type squashfs (ro,nodev,relatime,x-gdu.hide)
/dev/sda1 on /boot/efi type vfat (rw,relatime,fmask=0077,dmask=0077,codepage=437,iocharset=iso8859-1,shortname=mixed,errors=remount-ro)
tmpfs on /run/snapd/ns type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,size=801120k,mode=755)
nsfs on /run/snapd/ns/docker.mnt type nsfs (rw)
nsfs on /run/snapd/ns/snap-store.mnt type nsfs (rw)
nsfs on /run/snapd/ns/ipfs-desktop.mnt type nsfs (rw)
tmpfs on /run/user/125 type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,size=801116k,mode=700,uid=125,gid=130)
gvfsd-fuse on /run/user/125/gvfs type fuse.gvfsd-fuse (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,user_id=125,group_id=130)
tmpfs on /run/user/1003 type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,size=801116k,mode=700,uid=1003,gid=1003)
gvfsd-fuse on /run/user/1003/gvfs type fuse.gvfsd-fuse (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,user_id=1003,group_id=1003)
tmpfs on /run/user/1000 type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,size=801116k,mode=700,uid=1000,gid=1000)
gvfsd-fuse on /run/user/1000/gvfs type fuse.gvfsd-fuse (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,user_id=1000,group_id=1000)
/dev/sdb1 on /media/nicholas/3e798148-4333-4add-ba6c-f4272c17263e type ext4 (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,uhelper=udisks2)
nicholas@mordor:~$
nicholas@mordor:~$ lsusb
Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
Bus 007 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
Bus 006 Device 013: ID 1c4f:0034 SiGma Micro Usb Mouse
Bus 006 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
Bus 005 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
Bus 001 Device 003: ID 14cd:6116 Super Top M6116 SATA Bridge
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
Bus 004 Device 002: ID 2a7a:6a18 CASUE CASUE USB Keyboard
Bus 004 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
Bus 003 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
nicholas@mordor:~$
nicholas@mordor:~$ ls /media/nicholas/
3e798148-4333-4add-ba6c-f4272c17263e
nicholas@mordor:~$
nicholas@mordor:~$
Perhas the external drive needs to formatted to FAT32?
USBoption withunetbootinand proceeded from there. About to reboot and try to boot from the USB drive. We shall see. – Nicholas Saunders Apr 22 '21 at 05:47unetbootinin this scenario. – Nicholas Saunders Apr 22 '21 at 07:04unetbootinwon't make an external SATA hdd (connected with USB cable) bootable, then the q is unanswerable @C.S.Cameron -- but that seems odd. I'd be more interested in a "live" option. – Nicholas Saunders Apr 22 '21 at 08:08