Assume I am using 4 workspaces and I incidentally need more, is there an automated process or, if impossible, an easy way to incidentally add more workspaces (instead of installing Ubuntu tweak etc. etc.).
- 83,767
- 11,732
-
http://www.webupd8.org/2010/08/how-to-add-delete-workspaces-in-compiz.html – A.B. Sep 19 '15 at 18:04
-
@JacobVlijm http://imgur.com/LaDYwGb Upvoted and Accepted, thanks for really nice answer – kernel_panic Sep 22 '15 at 02:19
-
Related: This old post had asked on "How to have more Workspaces created/removed Automatically?" with two different answers. Then again, the older answers are likely less satisfied when compared to the newer answers here. – Dec 09 '15 at 09:13
2 Answers
Automatically set the number of workspaces; add and remove columns and rows, depending on your needs
Below a version of a (the) backround script that will automatically add workspaces if you entered the last column or row of your workspace-matrix.
This is how it works:
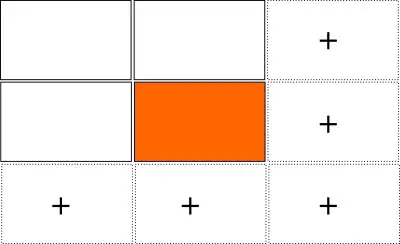
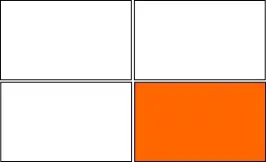
If you arrive at the last column or row, additional viewports are added:
If your workspaces are unused for 5-10 seconds and there are no windows on it, the additional workspaces will be removed again. You will however always keep one extra row below, and one extra column right of your current viewport:
The script:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import time
import math
# --- set default workspaces below (horizontally, vertically)
hsize = 2
vsize = 2
# --- set the maximum number of workspaces below
max_ws = 10
def set_workspaces(size, axis):
subprocess.Popen([
"dconf", "write", "/org/compiz/profiles/unity/plugins/core/"+axis,
str(size)
])
def get_res():
resdata = subprocess.check_output(["xrandr"]).decode("utf-8").split()
curr = resdata.index("current")
return (int(resdata[curr+1]), int(resdata[curr+3].replace(",", "")))
def wspace():
try:
sp = subprocess.check_output(["wmctrl", "-d"]).decode("utf-8").split()
return ([int(n) for n in sp[3].split("x")],
[int(n) for n in sp[5].split(",")])
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
pass
def clean_up(curr_col, curr_row):
try:
w_list = [l.split() for l in subprocess.check_output(["wmctrl", "-lG"]).decode("utf-8").splitlines()]
xpos = max([math.ceil((int(w[2])+span[1][0])/res[0]) for w in w_list])
min_x = max(xpos, curr_col+1, hsize)
if xpos >= hsize:
set_workspaces(min_x, "hsize")
else:
set_workspaces(min_x, "hsize")
ypos = max([math.ceil((int(w[3])+span[1][1])/res[1]) for w in w_list])
min_y = max(ypos, curr_row+1, vsize)
if ypos >= vsize:
set_workspaces(min_y, "vsize")
else:
set_workspaces(min_y, "vsize")
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
pass
res = get_res()
t = 0
while True:
span = wspace()
if span != None:
cols = int(span[0][0]/res[0]); rows = int(span[0][1]/res[1])
currcol = int((span[1][0]+res[0])/res[0])
if all([currcol == cols, cols*rows < max_ws]):
set_workspaces(cols+1, "hsize")
currrow = int((span[1][1]+res[1])/res[1])
if all([currrow == rows, cols*rows < max_ws]):
set_workspaces(rows+1, "vsize")
if t == 10:
clean_up(currcol, currrow)
t = 0
else:
t = t+1
time.sleep(1)
How to use
- Copy the script below into an empty file, save it as
add_space.py In the head section of the script, edit the lines if you like other settings (maximum number of workspaces, default matrix e.g. 2x2):
# --- set default workspaces below (horizontally, vertically) hsize = 2 vsize = 2 # --- set the maximum number of workspaces below max_ws = 10Test- run it by the command:
python3 /path/to/add_space.pyIf all works fine, add it to your startup applications: Dash > Startup Applications > Add the command:
/bin/bash -c "sleep 15 && python3 /path/to/add_space.py`
Note
As always, the script is extremely "low on juice", and does not add any noticeable load to your processor.
Explanation
The story below is a bit complicated and mostly an explanation on the concept and the procedure, rather than the coding. Only read if you're interested.
How to calculate the needed workspaces (example columns)
The output of wmctrl -d looks like:
0 * DG: 3360x2100 VP: 1680,1050 WA: 65,24 1615x1026 N/A
In the output, VP: 1680,1050 gives us information on where we are on the spanning workspace (the matrix of all viewports). This information is only useful if we also have the screen's resolution, since e.g. 1680 could be the width of two (unlikely, but still) or one time the screen.
Luckily, we can parse out the screen's resolution from the command xrandr.
Then if we know the screen's x-size is 1680 and we currently are on VP: 1680,1050, we know we are on the second column in the workspace's matrix. Since we also know the size of the total matrix (DG: 3360x2100, also from the output of wmctrl -d), we know the current matrix includes two columns (3360/1680), and we are on the "last" one.
The script will then send an instruction to add a column to the matrix by the command:
dconf write /org/compiz/profiles/unity/plugins/core/hsize <current_viewport_column+1>
This is the principle.
How to calculate the workspaces to remove (example columns)
Once per 10 seconds, the script runs the command to list all currently opened windows, with the command:
wmctrl -lG
This gives us information on the window's position also, looking like:
0x04604837 0 3425 24 1615 1026 jacob-System-Product-Name Niet-opgeslagen document 2 - gedit
In the output, 3425 is the x-position of the window. This figure is however relative to the current workspace (left side). To know the absolute position of the window (x-wise) in the workspace-matrix, we have to add the first number of the current viewport information (e.g. VP: 1680,1050, from the output of wmctrl -d).
Let's however, for simplicity reasons, assume we are on viewport 1,1 (topleft viewport), so the window's relative position equals its absolute position.
Since the screen's resolution is 1680, we know the window is on column 3425/1680, rounded up, since everything between 3360 and 5040 is on the same column in the matrix (between 3 and 4 times the resolution). For proper calculation we use math.ceil() (python)
Since the script also practices the rule to always have an extra workspace on the right/below, we need to set the number of columns to the highest value of:
- the current workspace column + 1
- the last column with a window on it
- the default number of columns, as set in the head of the script
And so the script does :)
The rows are managed in exactly the same procedure.
- 83,767
-
1
-
-
-
-
2@kernel_panic Wow, thanks :) I am actually thinking of making it a ppa, like this one: askubuntu.com/a/608295/72216, and this one: askubuntu.com/a/560734/72216, finally (in future) merging all three into one "workspace_tools" application where they can be set as options or something like that :). – Jacob Vlijm Sep 22 '15 at 07:25
-
Three things that i think would be nice in such a "workspace_tools" is 1) Browsing remote desktops along with workspaces, 2) Predefined Properties Workspaces 3) Save Workspace State – kernel_panic Sep 22 '15 at 12:09
-
-
1@JacobVlijm I would delete the old answer from here for reasons of brevity: it'll still be visible in the edit history for those who're interested... – Fabby Dec 10 '15 at 11:50
-
@Fabby Completely agreed, since the new answer replaces the old one, and if I remember well, there wasn't much voting before this version of the answer. Thanks for the suggestion! – Jacob Vlijm Dec 10 '15 at 15:00
-
1You're welcome... You should drop by the chat room and tox more often! :P – Fabby Dec 10 '15 at 16:01
-
Technically, there is no shortcut for resizing workspaces, but you can use the simple script bellow and bind it to a shortcut.
- Take the script bellow, save it in the
.local/share/applicationsfolder , or wherever you prefer. - Make sure the script is made executable with
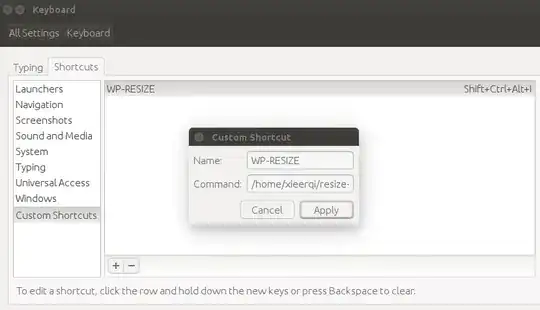
chmod 755 /path/to/script - Bind it to a shortcut in System Settings -> Keyboard -> Shortcuts -> Custom Shortcuts
For example, I have this setup:
The script is bound to ShiftCtrlAltI. But CtrlAltI could work too. I give full path to the script, which is
/home/xieerqi/resize-workspaces.sh
And here's how it should look like:
Script
#!/bin/bash
# Author : Serg Kolo
# Date: Sept 19, 2015
# Purpose: simple script to resize
# unity workspaces
# Written for: http://askubuntu.com/q/676046/295286
HEIGHT=$(gsettings get org.compiz.core:/org/compiz/profiles/unity/plugins/core/ hsize)
WIDTH=$(gsettings get org.compiz.core:/org/compiz/profiles/unity/plugins/core/ vsize)
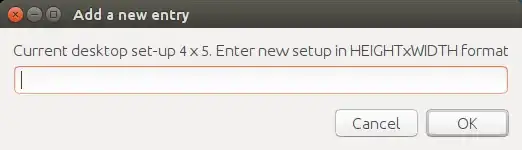
NEWSIZE=$(zenity --entry --text="Current desktop set-up $HEIGHT x $WIDTH. Enter new setup in HEIGHTxWIDTH format" --width=250 | tr 'x' ' ' )
ARRAY=( $NEWSIZE )
[ -z ${ARRAY[1]} ] && exit
gsettings set org.compiz.core:/org/compiz/profiles/unity/plugins/core/ hsize ${ARRAY[0]}
gsettings set org.compiz.core:/org/compiz/profiles/unity/plugins/core/ vsize ${ARRAY[1]}
Very simple to use, very simple to set up
- 90,397
- 105,154
- 20
- 279
- 497