Why is everybody keep mentioning to disable Fast Boot on Windows 8 if you have installed alongside Ubuntu? Is it something that is recommended only for UEFI machines or is it a suggestion for Legacy BIOS machines as well? Is it because it makes the Windows partition inaccessible from Linux or there is another more serious reason to disable it?
3 Answers
Fast boot explained with an image:
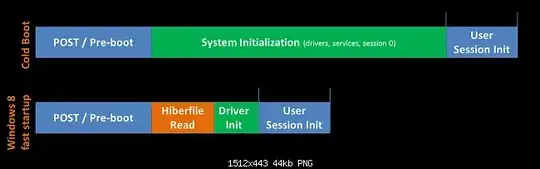
During fast boot the system loads the hiberfile and does not use the files on the filesystem.
So the biggest problem, and the worst problem you can have on a computer, is data loss: if you create a shared NTFS data partition the hibernation may maintain the file structure so if you try to save a file from Linux into the NTFS partition it will get lost on Windows reboot as it only remembers the old file structure. See this Ubuntu Forums thread for more information.
That alone is reason enough to never touch fast boot in a dual boot setup.
Two relevant discussions from Super User:
Hibernating and booting into another OS: will my filesystems be corrupted?
What do I have to take care of when hibernating both Ubuntu and Windows (dual-boot environment) Make sure to take note of this answer by Gilles.
In general: if a disc is mounted when using fast boot, Windows puts this disc and its content in a hiberfile. Any changes made to the system are gone when the hiberfile is restored. This includes mounted external discs. Ubuntu will refuse to mount a disc that has a hiberfile.
One of the bad messages you see in these topics is getting a "disc has errors" when booting Windows.
-
2I did not understand anything in your answer. Please dumb it down a bit. – Benjamin Hubbard Apr 21 '14 at 15:30
-
I think what he is trying to tell is that if you are going to create and save for a example a file on a NTFS partition that you created and this partition is shared with Ubuntu and Windows, and you save this file while you are using Ubuntu then Windows will delete this file because inside the hibernation file that Windows creates in Fast Boot mode it is saved the old file structure and this one doesn't contain the new file that you created. – und3rd06012 Apr 21 '14 at 16:14
-
@Rinzwind So I guess if you don't have a shared partition is it ok to have the Fast Boot mode enabled?Eitherway Ubuntu doesn't let me access the NTFS partition that Windows is installed on. – und3rd06012 Apr 21 '14 at 16:25
-
If I have an external hard drive and I make changes to this hard drive from Ubuntu while Fast Boot is on will this problem affect the files of my external hard drive? – und3rd06012 Apr 21 '14 at 16:26
-
Two related questions on Super User: Hibernating and booting into another OS: will my filesystems be corrupted?, What do I have to take care of when hibernating both Ubuntu and Windows – Jan Fabry Apr 21 '14 at 17:35
-
3@Rinzwind: Not at all! I think the best advice comes from the second question: "always unmount the shared partition(s) before hibernating". Only one OS should be the writer of a partition at any time, and hibernation (either by Windows or by Linux!) keeps that OS in charge. – Jan Fabry Apr 21 '14 at 17:45
-
@JanFabry I don't get one thing.Some answers mention that the users are hibernating Windows and they access the Windows partition from Ubuntu.How do they do that?When I am trying to do that I get an error message from Ubuntu saying that it can't mount the partition because it is "probably hibernated".Do older versions of Ubuntu let users mount the hibernated partition of Windows?Also can somebody answer me to the question that I made for the external drive? – und3rd06012 Apr 21 '14 at 21:38
-
@underdog012 external drive: if unmounted fine, if mounted trouble. – Rinzwind Apr 22 '14 at 07:05
-
@Rinzwind, So do you mean that if we have "Fast Boot" setting on but never use it (e.g. we only use full restart and not fast boot), there would be no problems? – Pacerier Apr 26 '15 at 22:46
-
Nope. Full restart means Windows will hibernate. – Rinzwind Apr 26 '15 at 22:52
-
1@Rinzwind, The article on SU http://superuser.com/a/496319/78897 seems to contradict that. Also, in the Windows help article (linked from that area of control panel), it claims "fast startup setting doesn't apply to restart". – Pacerier Apr 26 '15 at 23:56
-
One of your few posts with a pretty graphic :) +1 – WinEunuuchs2Unix Oct 26 '19 at 17:24
Fast boot in Windows 8 is a way to boot the system faster because the needed data to boot (Drivers, User session, etc..) are stored in a hibernation file (hiberfile) and are loaded when the boot process begins, saving the user between 40% and more boot time.
Since Hibernation mode is a way to "freeze" whatever you were doing before shutdown and loading it again when you start the computer (this includes opened apps, sessions, drivers, the last office doc you were editing...) it creates a problem when you want to copy stuff from Ubuntu to Windows after a hibernation, or "fast boot" as it is called on Windows 8 because anything that changes between hibernating and booting again is lost.
Basically, if you shutdown Windows 8 (hibernate mode) and then go to Ubuntu and try to copy something over to Windows 8 like an mp3 file (assuming Ubuntu does not throw any warnings about it being in hibernation mode), when you boot Windows 8 again, the mp3 file will not be there because it was not frozen during the shutdown procedure you did on Windows 8 before going to Ubuntu. Since the mp3 file was not there BEFORE shutting down Windows 8, it was not saved in the hiberfile and thus will not be restored after you do a Fast boot to load Windows.
There are however 2 ways to disable this so you can share files between both systems as described in Installing Ubuntu Alongside a Pre-Installed Windows with UEFI
- 211,503
-
So are you suggesting that since it's fully restored, yes you lose some files, but the there would be no corruptions in the filesystem? – Pacerier Apr 26 '15 at 22:44
-
Are you sure? It makes no sense. Hibernation should not touch the whole HD, just some system files, etc. It you copy a mp3 to a random folder, like C:\i like music\ nothing should happen after reboot. – Lombas Sep 16 '15 at 14:27
-
Hi lombass, correct hibernation should not touch any other files or areas of the hdd but the "new" is not the normal hibernation, it actually freezes the state of the hdd. I tried (when I tested this) to copy files to c:, program files, document settings and even created a folder in c:. No luck, all disappeared after rebooting through windows. – Luis Alvarado Sep 17 '15 at 13:23
-
@LuisAlvarado How about if Windows is installed on C but the file was moved from Ubuntu to D instead? – M J Jul 05 '17 at 18:30
-
@Joraid then you are able to copy them. IT only freezes where the system is in. So basically only the C drive. The D or any letter are safe to use for this. – Luis Alvarado Jul 05 '17 at 21:39
-
@LuisAlvarado thank you for your reply. You seem like you know your stuff. Could we use a shared partition to store and use user's files such as desktop, documents, music etc between win and ubuntu? It seems I can access windows files from Ubuntu, but not the other way around due to ntfs and ext plus permission issues among both OSes. – M J Jul 05 '17 at 23:48
-
1@Joraid Yes you can use a shared partition, typically partitioned in fat32 for compatibility between both systems (Since fat32 does not have the overhead of a permission layout like NTFS) – Luis Alvarado Jul 06 '17 at 00:39
-
With fast boot enabled, windows locks down the drives. I had trouble installing Kubuntu on my new laptop because of this. I got around it by opening partition manager while running off of the Live USB and shredding the windows partitions. Worked for me because I wanted to get rid of windows altogether, but would be a problem if I had wanted a dual boot system.
- 11